Category
- Best Peptides for muscle growth
- Geno Pharma Domestic Warehouse 2 (Canada&USA)
- GPH(Domestic Shipping US) Warehouse 1
- Human Pharma Premium
- Phar Labs Premium-Select
- Steroids on Sale USA, Real Steroids Online
- New arrivals in USA
- Most popular steroids in USA
- Antiestrogens / Gonadotropins
- Bangkok Steroid USA
- Biopharma Steroid USA
- British Dragon
- Anabolic Steroids for Horses
- Fat-burners
- Gen Pharma USA
- Medical Pharma Steroid USA
- Medical Tech Steroid USA
- Novocrine Steroids
- HGH USA
- Omega Labs Steroid USA
- Rotterdam Steroids USA
- SARMs USA
- Sciroxx
- Sydgroup Steroid USA
- Big vetenary Steroid USA
- Watson Steroids
- XT Labs Steroids
Most Popular steroids USA
-
 Primobolan for sale 100mg 10 ml Human Pharma in USA
$115.00
Primobolan for sale 100mg 10 ml Human Pharma in USA
$115.00 -
 NPP Steroid 100mg 10 ml Premium Domestic USA
NPP Steroid 100mg 10 ml Premium Domestic USA
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$80.00Current price is: $80.00. -
 Anavar for Sale in USA – 10mg 80 Tabs GPH-Premium
Anavar for Sale in USA – 10mg 80 Tabs GPH-Premium
$110.00Original price was: $110.00.$80.00Current price is: $80.00. -
 Buy Anavar 10mg – Purchase Geno Pharma
$99.00
Buy Anavar 10mg – Purchase Geno Pharma
$99.00 -
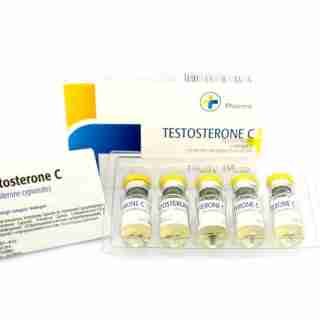
 Testosterone Cypionate Buy 300mg 10ml Geno Pharma
$99.00
Testosterone Cypionate Buy 300mg 10ml Geno Pharma
$99.00 -
 Buy Testosterone E 300mg 10 ml Geno Pharma Domestic USA/CA
$99.00
Buy Testosterone E 300mg 10 ml Geno Pharma Domestic USA/CA
$99.00 -
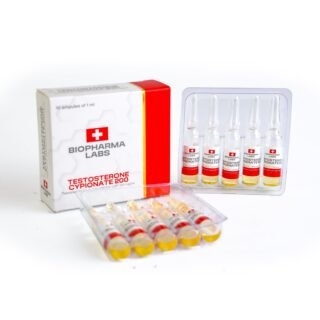
 Testosterone Cypionate 200 Biopharma 10 amp
Testosterone Cypionate 200 Biopharma 10 amp
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$72.00Current price is: $72.00. -
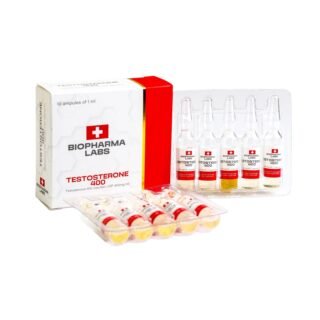
 Testosterone 400 Biopharma 10 Ampoules
Testosterone 400 Biopharma 10 Ampoules
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$75.00Current price is: $75.00. -
 Eq 300 steroid Rotterdam 10ml
Eq 300 steroid Rotterdam 10ml
$79.00Original price was: $79.00.$69.00Current price is: $69.00. -
 Steroid Deca Geno Pharma 300mg 10ml
Steroid Deca Geno Pharma 300mg 10ml
$110.00Original price was: $110.00.$99.00Current price is: $99.00. -
 Boldenone Cypionate 200 mg / 10 mL Geno Pharma
Boldenone Cypionate 200 mg / 10 mL Geno Pharma
$90.00Original price was: $90.00.$85.00Current price is: $85.00. -
 Somatrox XT Labs 150 IU x 10 vials (15 ui each)
Somatrox XT Labs 150 IU x 10 vials (15 ui each)
$450.00Original price was: $450.00.$350.00Current price is: $350.00.

Winstrol (Stanozolol) 100mg/ml 10 ml Medical Pharma
$93.00
Androstanazol; Androstanazole; Estanazol; Estanozolol; Methylstanazole; Metistanazol; NSC-43193; Stanotsololi; Stanozololis; Stanozololum; Stanozolum; Sztanozolol; Win-14833. 17α-Methyl-2′H-5α-androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol.
Share this page:
- Share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Share on Tumblr (Opens in new window) Tumblr
Winstrol (Stanozolol) 100mg/ml 10 ml Medical Pharma Steroids in USA
C21H32N2O = 328.5.
CAS — 10418-03-8.
ATC — A14AA02.
ATC Vet — QA14AA02.
NOTE. The following terms have been used as ‘street names’ or slang names for various forms of stanozolol: Iron Brew.
Pharmacopoeias. In China and US.
USP 31(Stanozolol). An odourless crystalline powder occurring in 2 forms; needles melt at about 155°and prisms at about 235°.
Insoluble in water; soluble 1 in 41 of alcohol, 1 in 74 of chloroform, and 1 in 370 of ether; slightly soluble in acetone and in ethyl acetate; soluble in dimethylformamide; very slightly soluble in benzene. Store in airtight containers. Protect from light.
Winstrol contains: 100mg
100 mg / ml Stanozolol
Pharmacologic category
Androgen.
Dosing: Adult
100mg, once every week.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Androgens are usually avoided in children with hereditary angioedema (below) because of their adverse effects, but they have been used when other treatments are ineffective. In the USA oral doses of stanozolol 1 mg daily, given only during an attack, have been used in children under 6 years of age, and up to 2 mg daily in those aged 6 to 12 years.
Slightly higher doses have been permitted in children in the UK.
Has not been used in the injected form in the pediatric population.
Dosing: Renal impairment
No dosage adjustment provided in manufacturer’s labeling; use with caution due to propensity to cause edema.
Dosing: Hepatic impairment
No dosage adjustment provided in manufacturer’s labeling; use with caution.
Use
Stanozolol has anabolic and androgenic properties, with other anabolic steroids, stanozolol has been used for breast cancer in postmenopausal women, and for anaemias, osteoporosis, and catabolic disorders. It has been given in oral doses of 2 mg every 8 to 12 hours, or 50 mg by intramuscular injection every 2 or 3 weeks.
In the management of hereditary angioedema, an initial oral dose of 2.5 to 10 mg daily has been given to prevent attacks. The dosage may then be reduced, according to the patient’s response; maintenance doses of 2 mg daily or on alternate days, or 2.5 mg three times weekly have been used successfully. For doses that have been used in children, see below.
Stanozolol raises serum concentrations of C1 esterase inhibitor and has been used successfully to prevent attacks of hereditary angioedema.
Stanozolol has been used in the treatment of vascular manifestations of Behçet’s syndrome. It has also been reported to promote fibrinolysis in vascular disorders, and has been tried in various conditions. However, most studies have been non-comparative and in small numbers of patients, and results have been variable.
Storage/Stability
Store in a dark, dry place at room temperature.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to stanozolol or any component of the formulation.
Men with carcinomas of the breast or with known or suspected carcinomas of the prostate; women who are or may become pregnant.
Documentation of allergenic cross-reactivity for androgens is limited. However, because of similarities in chemical structure and/or pharmacologic actions, the possibility of cross-sensitivity cannot be ruled out with certainty.
Warnings/Precautions
Gynecomastia: May cause Gynecomastia.
Hepatic effects: Prolonged use and/or high doses may cause peliosis hepatis or liver cell tumors, which may not be apparent until liver failure or intra-abdominal hemorrhage develops. Discontinue in case of cholestatic hepatitis with jaundice or abnormal liver function tests.
Venous thromboembolism: Venous thromboembolic events, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), have been reported with testosterone products. Evaluate patients with symptoms of pain, edema, warmth, and erythema in the lower extremity for DVT and those with acute shortness of breath for PE. Discontinue therapy if a venous thromboembolism is suspected.
Disease related concerns:
Breast cancer: Use with caution in patients with breast cancer; may cause hypercalcemia by stimulating osteolysis.
Edematous conditions: Use with caution in patients with conditions influenced by edema (eg, cardiovascular disease, migraine, seizure disorder, renal impairment); may cause fluid retention.
Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with hepatic impairment.
Pregnancy risk factor
X
Category X: Studies in animals or human beings have demonstrated fetal abnormalities, or there is evidence of fetal risk based on human experience, or both, and the risk of the use of the drug in pregnant women clearly outweighs any possible benefit. The drug is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant.
Pregnancy considerations
Use is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant; masculinization of the fetus has been reported.
Lactation
Excretion in breast milk unknown/not recommended
Breast feeding considerations
It is not known if stanozolol is excreted in breast milk. Due to the potential for serious adverse reactions in the nursing infant, breast-feeding is not recommended.
Adverse reactions
As for androgens and anabolic steroids in general. As with other 17α-alkylated compounds stanozolol may produce hepatotoxicity, and liver function should be monitored. It is probably best avoided in patients with hepatic impairment, and certainly if this is severe. Haematocrit and haemoglobin concentrations should also be monitored.
Because of its androgenic effects it has been recommended that stanozolol should not be used to treat hereditary angioedema in premenopausal women except in life-threatening situations.
Effects on the kidney. Renal failure with cholestatic jaundice has been reported with Stanozolol.
Effects on the liver. Cholestatic jaundice has been reported with stanozolol, in some cases with acute tubular necrosis and renal failure.
Effects on the nervous system. Benign intracranial hypertension developed in an elderly woman receiving stanozolol; CSF pressure returned to normal after stanozolol was stopped.
Porphyria. Stanozolol is considered to be unsafe in patients with porphyria because it has been shown to be porphyrinogenic in animals.
Frequency unknown.
Cardiovascular: Edema.
Central nervous system: Depression, excitation, insomnia.
Dermatologic: Acne (females and prepubertal males).
Also reported in females: Hirsutism, male-pattern baldness.
Endocrine & metabolic: Electrolyte imbalances, glucose intolerance, gonadotropin secretion inhibited, gynecomastia, HDL decreased, LDL increased, libido changes.
Also reported in females: Clitoral enlargement, menstrual irregularities.
Genitourinary:
Prepubertal males: Increased or persistent erections, penile enlargement
Postpubertal males: Bladder irritation, epididymitis, impotence, oligospermia, priapism (chronic), testicular atrophy, testicular function inhibited
Hematologic: Prothrombin time increased, suppression of clotting factors.
Hepatic: Alkaline phosphatase increased, ALT increased, AST increased, bilirubin increased, cholestatic jaundice, hepatic necrosis (rare), hepatocellular neoplasms, peliosis hepatis (with long-term therapy).
Neuromuscular & skeletal: CPK increased, premature closure of epiphyses (in children).
Renal: Creatinine excretion increased.
Metabolism/Transport effects
None known.
Drug interactions
Corticosteroids, Warfarin and Antidiabetic agents.
Test interactions
May suppress factors II, V, VII, and X; may increase PT; may decrease thyroxine-binding globulin and radioactive iodine uptake.
Monitoring parameters
Liver function tests, cholesterol profile, hemoglobin/hematocrit; INR/PT in patients on anticoagulant therapy.
Children: Radiographs of left wrist and hand every 6 months (to assess bone maturation).
Adult females: Signs of virilization (deepening voice, hirsutism, acne, clitoromegaly); urine and serum calcium in women with breast cancer.
Dosage forms
Injectable form 50mg/ml and 100mg/ml.
Anatomic Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification
A14AA02.
Mechanism of action
Anabolic steroid derived from dihydrotestosterone (DHT) sharing similar properties, allegedly having much more anabolic potency with less androgenic effects. Also it is known for having a much longer half-life with less protein binding affinity than DHT.
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics
Stanozolol can be detected up to 20 days in blood, half-life is estimated to be around 7 days but can vary widely depending on route of administration (oral, intramuscular), even with the same route, highly variable absorption between subjects (human and animals) has been a common problem.
Metabolism: hepatic
Elimination: renal
Buy anabolic steroids online in USA.
Related products
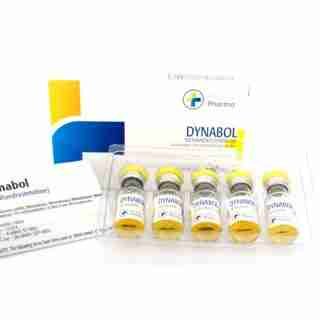
Dynabol Buy Online in USA 100mg/ml 10 ml Medical Pharma
$93.00Add to cartMetandienone (pINN); Metandienon; Metandienona; Métandiénone; Metandienoni; Metandienonum; Methandrostenolone; NSC-42722. 17β-Hydroxy-17α-methylandrosta-1,4 dien-3-one. Метандиенон.
C20H28O2 = 300.4.
CAS — 72-63-9.
ATC — A14AA03; D11AE01.
ATC Vet — QA14AA03; QD11AE01.
NOTE. The following terms have been used as ‘street names’ or slang names for various forms of Methandienone: Iron Brew.
Pharmacopoeias. In Pol
Deposteron Testosterone Cypionate for sale 250mg/ml 10 ml M P Buy in USA
$93.00Add to cartDeposteron
C27H40O3 = 412.6.
CAS — 58-20-8.
ATC — G03BA03.
ATC Vet — QG03BA03.USP 31(Testosterone Cypionate). A white or creamy-white, crystalline powder, odourless or has a slight odour. Insoluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, in dioxan, and in ether; soluble in vegetable oils. Protect from light.
Testerone C contains: 250mg.
⦁ 250mg/ml Testosterone Cypionate.
Anavar For Sale Online 15mg/100tabs MP | Purchasing Anavar US
$99.00Add to cartAnavar (Oxandrolone) 15mg 100 Tablets – Medical Pharma
Anavar (Oxandrolone) 15mg by Medical Pharma is a high-quality anabolic steroid known for its muscle-preserving and performance-enhancing properties. With 100 tablets per bottle, each containing 15mg of Oxandrolone (NSC-67068, SC-11585), it supports lean muscle retention, fat loss, and recovery while minimizing water retention. Its mild androgenic profile makes it a preferred choice for both men and women looking for effective yet controlled performance enhancement.
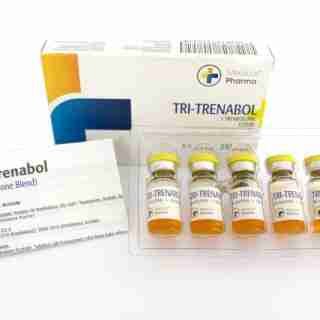
Tri Trenabol 150mg/ml 10 ml Trenbolone Blend – Medical Pharma
$93.00Add to cartTrenbolone Acetate
Trenbolone Acetate; Acetato de trenbolona; RU-1697; Trenbolone, Acétate de; Trenboloni Acetas; Trienbolone Acetate. 17β-Hydroxyestra-4,9,11-trien-3-one acetate.
Pay with WISE APP or Remitly
Pay with WISE App or Remitly
Fast money transfers from USA for fast delivery of steroids
Secure delivery in USA
100% reliable shipping in USA
24x7 Support
Online 24 hours
Low cost delivery
Great shipping prices in USA
BULK ORDER DISCOUNT
If you are a reseller in the USA you can get a special DISCOUNT, we can give you up to 50% or more on bulk orders. If you want to make a bulk order, we can negociate for orders of over USD$4,000, contact us by email.
Steroids info