Category
- Human Pharma Premium
- Phar Labs Premium
- Steroids on Sale USA, Real Steroids Online
- New arrivals in USA
- Most popular steroids in USA
- Antiestrogens / Gonadotropins
- Bangkok Steroid USA
- Biopharma Steroid USA
- British Dragon
- D & H Denkall Steroid USA
- Fat-burners
- Gen Pharma USA
- Medical Pharma Steroid USA
- Medical Tech Steroid USA
- Novocrine Steroids
- HGH USA
- Omega Labs Steroid USA
- Rotterdam Steroids USA
- SARMs USA
- Sciroxx Steroid USA
- Sydgroup Steroid USA
- Big vetenary Steroid USA
- Watson Steroid For Sale
- XT Labs Steroids
Most Popular steroids USA

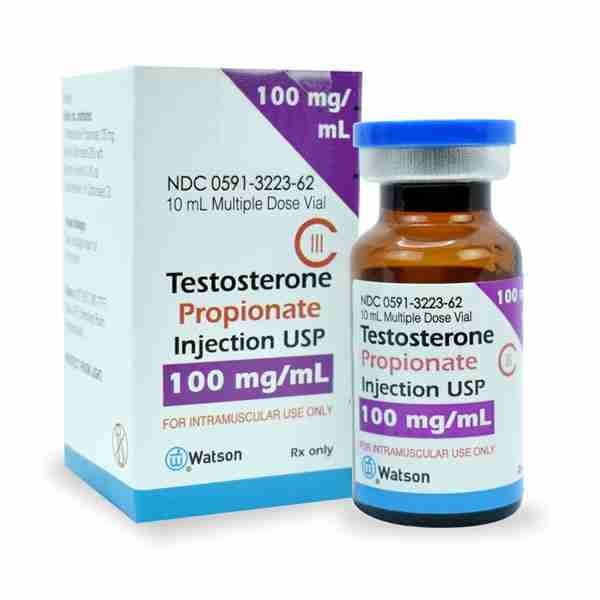
Testosterone Propionate 100mg 10ml – Watson Steroid in USA
$73.00
Injectable Oily Solution.
Deep intramuscular route.
Formula:
Each 1 mL of injectable oily solution contains: Testosterone Propionate 100mg
Share this page:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
Testosterone Propionate 100mg 10ml – Watson Steroid in USA
Mechanism of action and Pharmacokinetics:
Testosterone is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, through the skin and oral mucosa. However, it undergoes extensive hepatic first pass metabolism when administered orally and is therefore usually administered intramuscularly, subcutaneously, or transdermally. In addition, the basic molecule of Testosterone has been modified to obtain orally active derivatives and prolong the duration of the effect. Alkylation of the 17a position produces derivatives that are metabolized more slowly in the liver and, for this reason, can be administered orally.
Esterification of the 17-hydroxyl group increases lipid solubility and leads to slower systemic absorption if administered by intramuscular injection. The rate of absorption of esters is related to the size of the ester group. Testosterone esters are hydrolyzed to testosterone after absorption.
Testosterone is approximately 80% bound to sex hormone binding globulin. 19-nostestosterone derivatives and 17α-methylated derivatives are characterized by reduced binding to this globulin. The plasma elimination half-life of testosterone ranges from 10 to 100 min.
It is primarily metabolized in the liver via oxidation at the 17-OH group with the formation of androstenedione, which is further metabolized to the weakly androgenic androstenolone and inactive etiocholanolone, which are excreted in the urine primarily as glucuronoconjugates and sulfates. Approximately 6% is excreted unchanged in the faeces after undergoing enterohepatic recirculation.
Testosterone is converted to the more active derivative Dihydrotestosterone in some target organs by the effect of 5a-reductase. The 19-nortestosterone derivatives are less sensitive to this enzyme. Small amounts of testosterone are aromatized in the body, leading to the formation of estrogen derivatives in the body. Derivatives with a saturated A-ring, such as Mesterolone, aromatize less to estrogen.
Indications:
• It is used in the treatment of male hypogonadism. It is usually used in combination with Testosterone Enanthate.
• It is used in acute renal failure in the form of oily solutions for intramuscular route, Topical route is used
• It is used as an adjuvant in postmenopausal breast carcinoma, some postmenopausal disorders and delayed puberty in children.
Posology:
• In male hypogonadism: In adults, in the form of oily solutions for intramuscular route, administered in doses of 10 – 50 mg, two or three times a week.
• In acute renal failure: in dosages of 25 mg/day, for a maximum of 10 days.
Contraindications:
Should be avoided in the following cases:
Pregnancy: There are reports of virilization of the female fetus after maternal treatment with Testosterone or Methyl Testosterone during pregnancy.
Breastfeeding: the use of Testosterones in nursing mothers should be avoided, due to the potential androgenic effect on the infant.
Porphyria: Androgens are not considered safe in patients with porphyria, although experimental evidence of porphyrinogenia is available.
Adverse reactions:
Testosterone and other androgens can produce side effects related to their androgenic and anabolic activities: increased retention of nitrogen, water and sodium, edema, increased vascularity of the skin, hypercalcaemia, impaired glucose tolerance and increased growth bone and skeletal weight.
Other effects include increased low density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, increased hematocrit, and increased fibrinolytic activity. Androgens can cause headache, depression, and gastrointestinal bleeding. It has been suggested that androgens can induce sleep apnea in predisposed patients.
Abnormal liver function test results have been described, and case reports of hepatotoxicity, including jaundice and cholestatic hepatitis, have been published. These adverse hepatic effects have been predominantly identified with the 17α-alkylated derivatives.
In men, high doses suppress spermatogenesis and produce degenerative changes in the seminiferous ducts. Priapism is a sign of excessive doses that is seen especially in elderly men.
Gynecomastia has been described. Androgens can cause prostatic hyperplasia and may accelerate the growth of malignant neoplasms of the prostate.
In women, the inhibitory action of androgens on ovarian activity and menstruation. Its continuous use produces symptoms of virilization, it is not reversible in all cases, even after discontinuation of treatment.
Boys experience signs of virilization: boys show early sexual development with phallic hypertrophy and more frequent erections, and girls show clitoral hypertrophy. Some guys may have Gynecomastia.
Cautions and warnings:
Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular diseases, renal or hepatic insufficiency, epilepsy, migraine, diabetes or other conditions that may be aggravated by possible fluid retention or induced edema: They will not be administered to patients with hypercalcaemia or hypercalciuria, and they will be used with caution. if there are diseases that pose a risk of their appearance, such as bone metastases. Patients with liver failure should not take 17α-alkylated derivatives, as these drugs increase the risk of hepatotoxicity; furthermore, they are totally contraindicated if the insufficiency is severe.
Androgens and anabolic steroids should be used with caution in pediatric patients due to masculinizing effects and premature epiphyseal closure, which can lead to linear growth inhibition and short stature. During treatment, monitoring of bone maturation is necessary.
It should not be administered during pregnancy due to the risk of virilization of the female foetus.
Androgens and anabolic steroids interfere with various laboratory tests, such as glucose tolerance and thyroid function.
Interactions:
Testosterone and other androgens and anabolic steroids have been reported to potentiate the activity of a number of drugs, with a consequent increase in toxicity. Affected drugs include cyclosporine, antidiabetics, levothyroxine and anticoagulants such as warfarin.
Resistance to the effects of neuromuscular blocking agents has also been described.
Use restrictions:
Do not use in case of hypersensitivity to some of its components; during pregnancy and breastfeeding period. Nor use in patients with arterial hypertension, or in patients with cardiovascular problems, liver and kidney dysfunction.
Overdose:
Adverse effects have often occurred at doses higher than those used therapeutically, these as a consequence of the illegal use of androgens and anabolic steroids by athletes. These effects include abnormal liver function test results and liver neoplasia, increased risk of cardiovascular disease, and decreased glucose tolerance.
They frequently induce states of zoospermia or oligospermia and testicular atrophy in men, and amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea in women. Gynecomastia is relatively common in men, as is virilization in women. Psychiatric disorders such as states of mania, hypomania, depression, aggressiveness and emotional lability have been described.
Buy Testosterone Propionate steroid online USA.
Related products
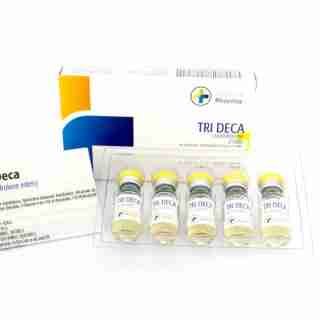
Tri Deca 300mg/ml 10 ml (3 Nandrolone esters) – Medical Pharma Steroid in USA
$103.00Add to cartC28H44O3 = 428.6.
CAS — 360-70-3.
ATC — A14AB01; S01XA11.
ATC Vet — QA14AB01; QS01XA11.Pharmacopoeias. In Eur.(see p.vii) and US.
Tri-Deca contains: 300mg
100 mg / ml Nandrolone Decanoate
100 mg / ml Nandrolone Phenylpropionate
100 mg / ml Nandrolone UndecanoateWinstrol (Stanozolol) 100mg/ml 10 ml Medical Pharma Steroids in USA
$93.00Add to cartAndrostanazol; Androstanazole; Estanazol; Estanozolol; Methylstanazole; Metistanazol; NSC-43193; Stanotsololi; Stanozololis; Stanozololum; Stanozolum; Sztanozolol; Win-14833. 17α-Methyl-2′H-5α-androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol.
Tri Trenabol 150mg/ml 10 ml (Trenbolone Blend) – Medical Pharma Steroid in USA
$93.00Add to cartTrenbolone Acetate
Trenbolone Acetate; Acetato de trenbolona; RU-1697; Trenbolone, Acétate de; Trenboloni Acetas; Trienbolone Acetate. 17β-Hydroxyestra-4,9,11-trien-3-one acetate.
Mastabol 100mg/ml 10ml – Medical Pharma Steroids Available in USA
$93.00Add to cartBa-29038; Boldenone Undecylenate (USAN); Boldénone, Undécylénate de; Boldenoni Undecylenas; 1-Dehydrotestosterone (boldenone); Undecilenato de boldenona. 17β-Hydroxyandrosta-1,4-dien-3-one 17-(undec-10-enoate). Болденона Ундециленат.
C30H44O3 = 452.7.
CAS — 846-48-0 (Boldenone); 13103-34-9 (Boldenone Undecenoate).
Equipoise contains: 200mg.
200 mg / ml Boldenone Undecylenate.Pharmacologic Category: Androgen.
Dosing
a) 1 mg/kg IM; may repeat in 1 week intervals (most will respond with one or two treatments).
b) 3 mg/kg IM; repeated at 1 week intervals (Robinson 1987).
Pay with Cash App or Remitly
Pay with Cash App or Remitly
Fast money transfers from USA for fast delivery of steroids
Secure delivery in USA
100% reliable shipping in USA
24x7 Support
Online 24 hours
Low cost delivery
Great shipping prices in USA
BULK ORDER DISCOUNT
If you are a reseller in the USA you can get a special DISCOUNT, we can give you up to 50% or more on bulk orders. If you want to make a bulk order, we can negociate for orders of over USD$4,000, contact us by email.