Category
- Best Peptides for muscle growth
- Geno Pharma Domestic Warehouse 2 (Canada&USA) (Ships in 1–3 days) Faster!
- GP(Domestic Shipping US) Warehouse 1
- Human Pharma Premium
- Phar Labs Premium-Select
- Steroids on Sale USA, Real Steroids Online
- New arrivals in USA
- Most popular steroids in USA
- Antiestrogens / Gonadotropins
- Bangkok Steroid USA
- Biopharma Steroid USA
- British Dragon
- Anabolic Steroids for Horses
- Fat-burners
- Gen Pharma USA
- Medical Pharma Steroid USA
- Medical Tech Steroid USA
- Novocrine Steroids
- HGH USA
- Omega Labs Steroid USA
- Rotterdam Steroids USA
- SARMs USA
- Sciroxx
- Sydgroup Steroid USA
- Big vetenary Steroid USA
- Watson Steroids
- XT Labs Steroids
Most Popular steroids USA
-
 Primobolan Pills 25mg 100 pills Domestic USA
Primobolan Pills 25mg 100 pills Domestic USA
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$85.00Current price is: $85.00. -
 Clenbuterol for Sale 40mcg 100 Tabs - GP Premium Domestic USA
Clenbuterol for Sale 40mcg 100 Tabs - GP Premium Domestic USA
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$65.00Current price is: $65.00. -
 Winstrol Tablets for Sale 10mg 100 pills GP Domestic
Winstrol Tablets for Sale 10mg 100 pills GP Domestic
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$75.00Current price is: $75.00.

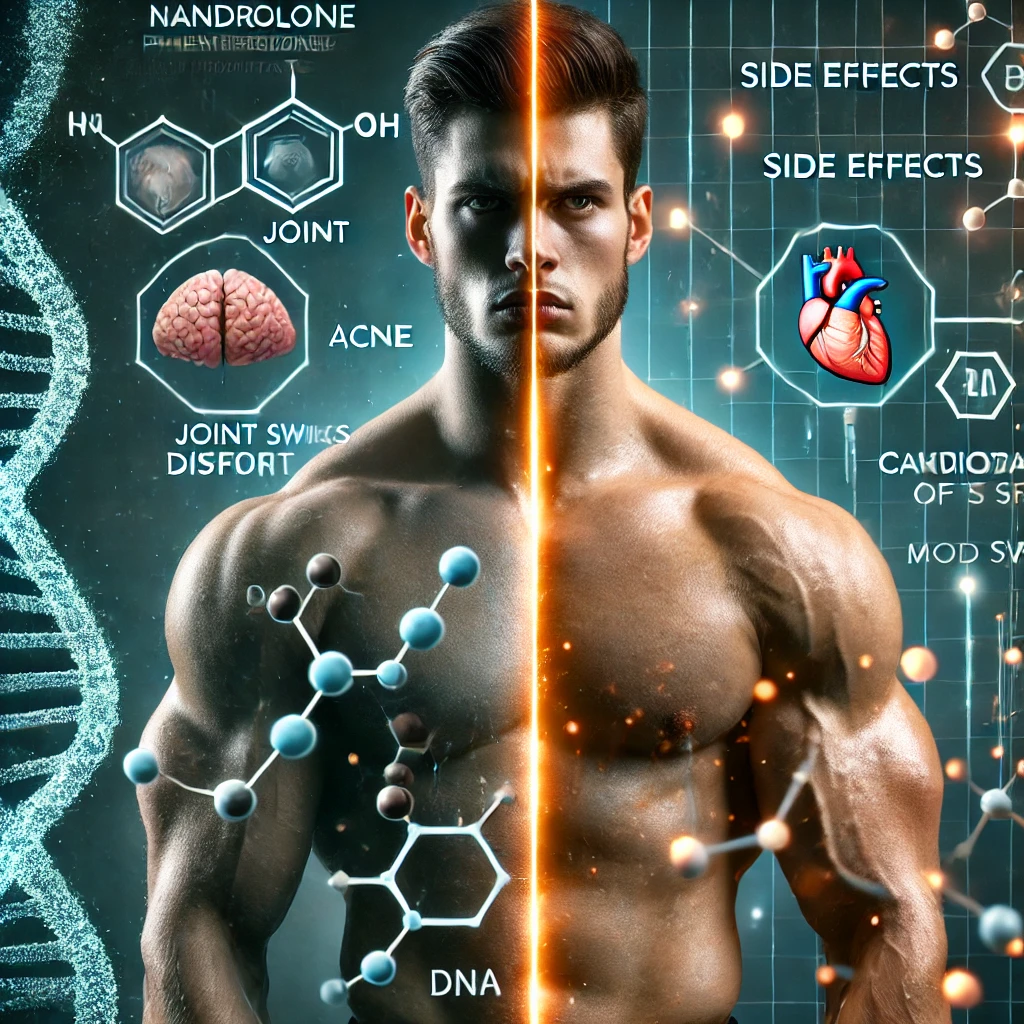
Nandrolone Phenylpropionate (NPP steroid) is a powerful anabolic compound widely used for muscle growth, strength enhancement, and faster recovery. However, beyond its well-known anabolic benefits, its effects extend deep into the body’s genetic expression, enzymatic reactions, and metabolic pathways.
Understanding NPP steroid side effects requires a multi-level analysis:
- Genetic and molecular regulation – How NPP affects gene expression and enzyme synthesis.
- Metabolic pathways – How it influences protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and energy production.
- Physiological and systemic side effects – The risks associated with cardiovascular, endocrine, and liver health.
This guide provides a detailed exploration of NPP’s impact on cellular function, genetic regulation, enzymatic activities, and overall metabolic health.
Get the Best Quality NPP Steroid Today! 💪🔥 Boost your muscle growth and recovery with premium NPP Steroid. Safe, reliable, and fast shipping! Order now and take your performance to the next level! 🚀🏋️♂️
Table of Contents
ToggleHow NPP Affects Genetic and Enzymatic Metabolic Reactions
Gene Expression and Androgen Receptor Activation
Once NPP enters the bloodstream, its lipophilic nature allows it to easily cross cell membranes and bind to androgen receptors (AR) within muscle and other tissues. This receptor-ligand complex then moves into the nucleus, where it binds to Androgen Response Elements (AREs) in the DNA, activating or suppressing genes that control muscle growth, recovery, and metabolism.
- Protein Synthesis Acceleration: Activation of genes encoding ribosomal proteins, myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs), and anabolic enzymes enhances muscle hypertrophy.
- Collagen Production Regulation: NPP also influences genes that regulate collagen and extracellular matrix proteins, which contribute to joint health and tendon strength.
- Epigenetic Modulation: Changes in DNA methylation and histone acetylation influence gene accessibility, allowing for fine-tuned anabolic responses.
By enhancing or repressing specific genes, NPP modifies the biochemical environment, ensuring that muscle-building pathways are upregulated while catabolic pathways (muscle breakdown) are suppressed.
Enzymatic and Metabolic Pathway Modulation
NPP-induced gene expression changes also increase enzyme synthesis, which enhances metabolic efficiency. Some of the key enzymatic and metabolic effects include:
- Amino Acid Transport & Protein Synthesis:
- Increased activity of mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) accelerates protein translation, leading to muscle fiber growth.
- Upregulation of leucine transporters improves amino acid absorption in muscle cells.
- Energy Production & ATP Regeneration:
- Increased mitochondrial biogenesis supports higher ATP levels, fueling intense workouts.
- Activation of AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) ensures optimal energy homeostasis.
- Lipid Metabolism & Fat Distribution:
- Enhanced fat oxidation results in a leaner physique.
- Increased lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity allows for better fat mobilization as an energy source.
By optimizing metabolic pathways, NPP enables faster recovery, greater endurance, and improved muscular efficiency.
Physiological and Systemic Side Effects of NPP Steroid

Despite its metabolic benefits, NPP steroid side effects can pose long-term risks, especially when used irresponsibly.
1. Hormonal Disruptions & Testosterone Suppression
One of the most significant effects of NPP steroid is its impact on natural testosterone production. Suppression occurs because exogenous androgens signal the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis to reduce endogenous testosterone production.
Potential effects include:
- Decreased libido & erectile dysfunction due to suppressed LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) production.
- Gynecomastia risk from excess estrogen conversion via aromatase enzyme activity.
- Testicular atrophy due to prolonged suppression of natural testosterone.
2. Cardiovascular Risks & Cholesterol Imbalances
NPP can negatively impact lipid metabolism, affecting cholesterol balance and cardiovascular health.
- Decreased HDL (“good” cholesterol) increases the risk of arterial plaque buildup.
- Increased LDL (“bad” cholesterol) raises the risk of atherosclerosis, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Elevated blood pressure due to fluid retention and altered nitric oxide levels.
How to mitigate cardiovascular risks:
- Omega-3 supplementation to counteract cholesterol imbalances.
- Regular cardiovascular exercise to support heart health.
- Blood pressure monitoring to detect issues early.
3. Liver & Kidney Function Considerations
Although NPP is not highly hepatotoxic, prolonged use or high doses can strain the liver and kidneys, especially when combined with other oral steroids or high-protein diets.
- Liver enzyme elevation (AST/ALT levels) can indicate inflammation or hepatotoxicity.
- Increased nitrogen waste from protein metabolism may stress kidney function.
How to protect liver and kidney health:
- Hydration – Drinking plenty of water aids in kidney function.
- Liver support supplements – Milk thistle and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) help protect liver cells.
- Periodic blood tests to monitor enzyme levels.
4. Psychological & Neurological Effects
NPP steroid can influence neurotransmitter levels, potentially leading to mood swings, aggression, or depression.
- Elevated dopamine levels may lead to increased confidence but also potential irritability.
- Serotonin suppression can contribute to mild depressive states post-cycle.
- Cognitive fog and fatigue due to neurotransmitter imbalances.
How to maintain psychological well-being:
- Proper cycle planning & gradual tapering to avoid severe post-cycle emotional swings.
- Healthy sleep patterns to support hormonal and neurological recovery.
- Supplementation with adaptogens like Ashwagandha or Rhodiola to stabilize mood.
How to Minimize NPP Side Effects
If you’re considering NPP steroid, it’s crucial to take steps to reduce potential risks while maximizing its benefits.
1. Follow Proper Dosage and Cycle Length
- Beginner dose: 200–300mg per week.
- Intermediate dose: 400–600mg per week.
- Cycle length: 8–12 weeks. Longer cycles increase side effects.
2. Implement a Strong Post-Cycle Therapy (PCT)
- Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate): Restores LH & FSH levels for natural testosterone production.
- Nolvadex (Tamoxifen): Helps prevent estrogenic side effects like gynecomastia.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
- Proper Nutrition – Prioritize lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbs to support recovery.
- Regular Blood Work – Monitor hormone levels, liver enzymes, and cholesterol.
- Joint & Ligament Care – Incorporate collagen supplements and mobility exercises.
Final Thoughts: The Science Behind NPP’s Effects
NPP steroid offers significant advantages for muscle growth, recovery, and athletic performance, but its side effects extend beyond simple hormonal changes. Its influence on gene expression, enzymatic reactions, and metabolic efficiency shapes how the body builds muscle, recovers from stress, and maintains systemic health.
To optimize results while reducing risks, it’s essential to follow evidence-based dosing, prioritize post-cycle recovery, and monitor physiological changes through regular health check-ups.
For those serious about using NPP steroid safely, this guide provides a comprehensive understanding of how it affects the body at the molecular, metabolic, and systemic levels—allowing for informed decisions and better performance outcomes.
Author
Dr. Daniel Martínez, MD is an endocrinologist and nutrition expert with 20+ years of experience in hormonal and metabolic health. He specializes in performance enhancement research and has co-authored a peer-reviewed study on medical applications in bodybuilding.
Share this page:
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window) Tumblr
Written by Steroids USA
Pay with WISE APP or Remitly
Pay with WISE App or Remitly
Fast money transfers from USA for fast delivery of steroids
Secure delivery in USA
100% reliable shipping in USA
24x7 Support
Online 24 hours
Low cost delivery
Great shipping prices in USA
BULK ORDER DISCOUNT
If you are a reseller in the USA you can get a special DISCOUNT, we can give you up to 50% or more on bulk orders. If you want to make a bulk order, we can negociate for orders of over USD$4,000, contact us by email.
Steroids info




Leave a Reply