Category
- Best Peptides for muscle growth
- Geno Pharma Domestic Warehouse 2 (Canada&USA) (Ships in 1–3 days) Faster!
- GP(Domestic Shipping US) Warehouse 1
- Human Pharma Premium
- Phar Labs Premium-Select
- Steroids on Sale USA, Real Steroids Online
- New arrivals in USA
- Most popular steroids in USA
- Antiestrogens / Gonadotropins
- Bangkok Steroid USA
- Biopharma Steroid USA
- British Dragon
- Anabolic Steroids for Horses
- Fat-burners
- Gen Pharma USA
- Medical Pharma Steroid USA
- Medical Tech Steroid USA
- Novocrine Steroids
- HGH USA
- Omega Labs Steroid USA
- Rotterdam Steroids USA
- SARMs USA
- Sciroxx
- Sydgroup Steroid USA
- Big vetenary Steroid USA
- Watson Steroids
- XT Labs Steroids
Most Popular steroids USA
-
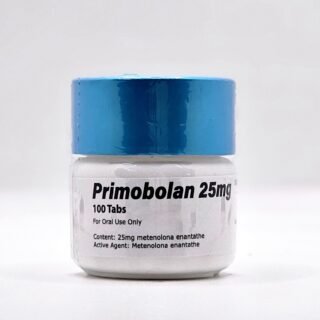
 Primobolan Pills 25mg 100 pills Domestic USA
Primobolan Pills 25mg 100 pills Domestic USA
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$85.00Current price is: $85.00. -
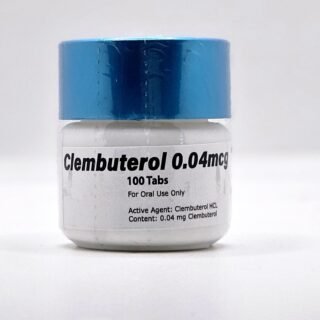
 Clenbuterol for Sale 40mcg 100 Tabs - GP Premium Domestic USA
Clenbuterol for Sale 40mcg 100 Tabs - GP Premium Domestic USA
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$65.00Current price is: $65.00. -
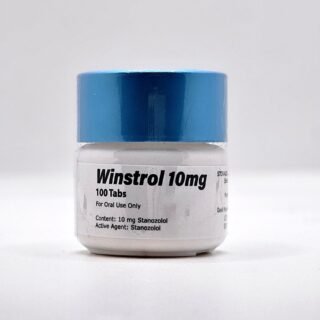
 Winstrol Tablets for Sale 10mg 100 pills GP Domestic
Winstrol Tablets for Sale 10mg 100 pills GP Domestic
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$75.00Current price is: $75.00.


Anabolic-androgenic steroids wield a potent influence over the body’s hormonal landscape, primarily aimed at muscle building. However, their far-reaching effects extend to mental state and sexual function, making this comprehensive guide an essential resource. Gain a thorough understanding of the multifaceted impacts that steroids exert on hormones, moods, emotions, and libido, empowering you to make informed choices.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnveiling the Foundation: Hormone Balance in the Body
For a nuanced grasp of steroid repercussions, a primer on natural hormone production proves essential. Fundamental glands and hormones include:
The Hypothalamus
Releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), triggering a cascade of other hormone releases.

The Pituitary Gland
Produces luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), vital for activating testosterone and sperm production.
The Testes
Synthesize testosterone, pivotal for male sexual function and muscle development.
The Adrenal Glands
Emit modest quantities of testosterone and cortisol, which factors into stress response.
Optimal levels of these hormones sustain physiological functions, sexual vitality, and overall well-being. Steroids, once introduced into the body, disrupt this delicate equilibrium.
The Mechanics Underlying Steroidal Influence on Hormones
Steroids leverage various mechanisms to impact hormones:
Superseding Normal Androgen Signaling
Exogenous steroids overpower signals for natural testosterone production, leading to suppressed output from the hypothalamus and testes.
Shifting Estrogen Balance
Steroids that aromatize can convert to estrogen via the aromatase enzyme, altering the androgen/estrogen equilibrium.
Disturbing the HPTA Axis
Elevated steroid levels confound the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis, the control center for testosterone production through LH and FSH release.
Engaging Androgen Receptors
Steroids directly activate androgen receptors in the brain and body, yielding discernible effects.
The upshot is a seismic shift in the hormonal milieu, exerting profound repercussions on diverse aspects of physical and mental health.
Hormonal Ramifications of Steroid Usage
Hormonal consequences associated with anabolic steroids comprise:
Suppressed Endogenous Testosterone
Severe inhibition of natural testosterone production and sperm counts.
Escalated Estrogen Levels
Disproportionate estrogen levels contribute to gynecomastia, water retention, and enlarged male breasts.
Elevated Cortisol
Heightened cortisol levels contribute to muscle breakdown, body fat accumulation, and mood disturbances.
Diminished Thyroid Hormone Levels
Reduced T3 levels, believed to impact fat metabolism, energy levels, and mental wellness.
Menstrual Irregularities
Women may grapple with erratic, absent, or altered menstrual cycles, signaling compromised fertility.
Hormonal Fluctuations
Cessation of steroid use prompts hormone fluctuations, impacting mood stability, energy levels, strength, and libido.
Carefully orchestrated cycles, bolstered by ancillary drugs, on-cycle support, and post-cycle therapy, are crucial for counteracting hormonal side effects and safeguarding the body’s delicate equilibrium.
The Psychological and Emotional Dimension of Steroid Usage
In tandem with physical repercussions, steroids can significantly influence mental well-being and emotions:
Emotional Fluctuations
Many users report mercurial mood patterns oscillating between irrational anger and depression.
Aggression and Hostility
Amplified testosterone levels and altered neurochemistry can lead to “roid rage,” often manifesting as aggression. Incidence of domestic violence is higher among users.
States of Euphoria
Reminiscent of bipolar disorder, some experience hyperactive, disinhibited states marked by heightened energy and impaired judgment.
Anxiety and Restlessness
Increased stress response, heightened excitability, repetitive thinking, and compromised social ease.
Sleep Disturbances
Cortisol and testosterone shifts can cause insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep and frequent waking.
Cognitive Impairment
Structural changes in the brain lead to memory deficits, reduced executive function, and difficulties in concentration.
Vigilant monitoring of mental health is imperative during steroid use. Mood stabilizers, therapeutic intervention, or discontinuation may be necessary if issues arise, especially if aggressive behavior endangers others.
Impact on Male Sexual Function and Desire
Steroid use exerts intricate effects on male sexual dynamics:
Dampened Libido
Contrary to myths, suppressed testosterone can lead to reduced sexual desire and erection frequency in some men.
Erectile Dysfunction
Paradoxically, hormonal imbalances can impair erectile function for certain users.
Impaired Fertility
Considerable suppression of sperm production and motility, often reversible post-cycle.
Testicular Contraction
Testes may shrink due to reduced LH and FSH stimulation, stemming from exogenous testosterone use.
Prostate Implications
Prostate stimulation can induce heightened urinary frequency, nocturnal, and dysfunction.
Nonetheless, some users report elevated libido, likely attributed to heightened androgen receptor stimulation within the central nervous system and psychological factors. Sexual effects manifest diversely.
Impact on Female Sexual Function and Desire
In the realm of women, steroids also cast a shadow on sexuality through multiple mechanisms:
Augmented Libido
Certain women note intensified libido, heightened sexual pleasure, and more vivid fantasies—attributes stemming from the androgenic nature of steroids.
Diminished Libido
Conversely, hormonal fluctuations may dampen female sexual desire via mechanisms that are still under scrutiny.
Clitoral Growth
Analogous to male sexual anatomy, steroid-induced clitoral growth is irreversible if severe.
Vaginal Transformations
Thinning vaginal walls might lead to tearing, spotting, and pain during intercourse, accompanied by decreased lubrication.
Menstrual Cycle Disruption
Distorted pituitary signaling and hypothalamic-ovarian axis contribute to amenorrhea, irregular cycles, and infertility.
As with men, steroids exert variable effects on female sexuality contingent on dosage, compounds, and sensitivity. Upholding a harmonious hormone balance remains pivotal.
Mitigating Hormonal, Emotional, and Sexual Aftereffects
Tactics to alleviate mental and sexual adversities encompass:
Prudent, brief cycle dosing with milder compounds.

Abstaining from orally-administered steroids that potentiate acute hormonal impact
Regular bloodwork assessment to ensure safe hormone levels
Incorporating ancillary drugs, including aromatase inhibitors
Enforcing comprehensive post-cycle therapy after discontinuation
Utilizing supplementary medications for sexual dysfunction or mental health concerns
Refraining from recreational drugs and alcohol during cycles
Adhering to sensible nutrition, cardiovascular activities, hydration, and a healthy lifestyle
Cultivating robust social support and fostering transparent communication with partners
Collaborating with medical professionals and therapists as deemed necessary
While steroids undeniably bolster performance, judicious usage mandates meticulous consideration of all potential mental and sexual implications in both genders. Ponder conscientiously, factor in ethical and health considerations, and then decide whether the venture align
Share this page:
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window) Tumblr
Written by Steroids USA
Pay with WISE APP or Remitly
Pay with WISE App or Remitly
Fast money transfers from USA for fast delivery of steroids
Secure delivery in USA
100% reliable shipping in USA
24x7 Support
Online 24 hours
Low cost delivery
Great shipping prices in USA
BULK ORDER DISCOUNT
If you are a reseller in the USA you can get a special DISCOUNT, we can give you up to 50% or more on bulk orders. If you want to make a bulk order, we can negociate for orders of over USD$4,000, contact us by email.
Steroids info