Category
- Best Peptides for muscle growth
- Geno Pharma Domestic Warehouse 2 (Canada&USA)
- GPH(Domestic Shipping US) Warehouse 1
- Human Pharma Premium
- Phar Labs Premium-Select
- Steroids on Sale USA, Real Steroids Online
- New arrivals in USA
- Most popular steroids in USA
- Antiestrogens / Gonadotropins
- Bangkok Steroid USA
- Biopharma Steroid USA
- British Dragon
- Anabolic Steroids for Horses
- Fat-burners
- Gen Pharma USA
- Medical Pharma Steroid USA
- Medical Tech Steroid USA
- Novocrine Steroids
- HGH USA
- Omega Labs Steroid USA
- Rotterdam Steroids USA
- SARMs USA
- Sciroxx
- Sydgroup Steroid USA
- Big vetenary Steroid USA
- Watson Steroids
- XT Labs Steroids
Most Popular steroids USA
-
 Primobolan for sale 100mg 10 ml Human Pharma in USA
$115.00
Primobolan for sale 100mg 10 ml Human Pharma in USA
$115.00 -
 NPP Steroid 100mg 10 ml Premium Domestic USA
NPP Steroid 100mg 10 ml Premium Domestic USA
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$80.00Current price is: $80.00. -
 Anavar for Sale in USA – 10mg 80 Tabs GPH-Premium
Anavar for Sale in USA – 10mg 80 Tabs GPH-Premium
$110.00Original price was: $110.00.$80.00Current price is: $80.00. -
 Buy Anavar 10mg – Purchase Geno Pharma
$99.00
Buy Anavar 10mg – Purchase Geno Pharma
$99.00 -
 Testosterone Cypionate Buy 300mg 10ml Geno Pharma
$99.00
Testosterone Cypionate Buy 300mg 10ml Geno Pharma
$99.00 -
 Buy Testosterone E 300mg 10 ml Geno Pharma Domestic USA/CA
$99.00
Buy Testosterone E 300mg 10 ml Geno Pharma Domestic USA/CA
$99.00 -
 Testosterone Cypionate 200 Biopharma 10 amp
Testosterone Cypionate 200 Biopharma 10 amp
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$72.00Current price is: $72.00. -
 Testosterone 400 Biopharma 10 Ampoules
Testosterone 400 Biopharma 10 Ampoules
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$75.00Current price is: $75.00. -
 Eq 300 steroid Rotterdam 10ml
Eq 300 steroid Rotterdam 10ml
$79.00Original price was: $79.00.$69.00Current price is: $69.00. -
 Steroid Deca Geno Pharma 300mg 10ml
Steroid Deca Geno Pharma 300mg 10ml
$110.00Original price was: $110.00.$99.00Current price is: $99.00. -
 Boldenone Cypionate 200 mg / 10 mL Geno Pharma
Boldenone Cypionate 200 mg / 10 mL Geno Pharma
$90.00Original price was: $90.00.$85.00Current price is: $85.00. -
 Somatrox XT Labs 150 IU x 10 vials (15 ui each)
Somatrox XT Labs 150 IU x 10 vials (15 ui each)
$450.00Original price was: $450.00.$350.00Current price is: $350.00.


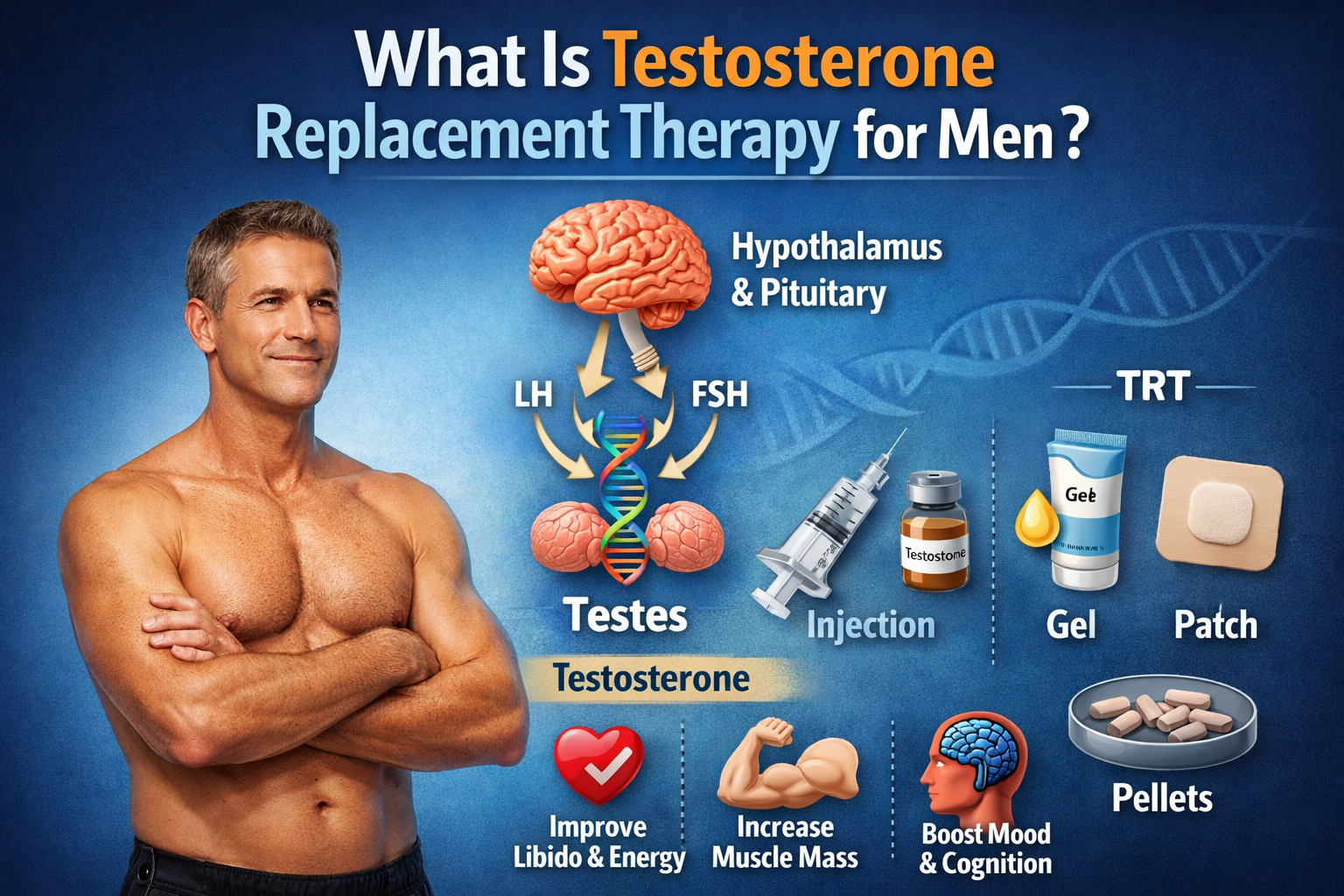
Anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS) provide muscle and performance enhancing effects highly sought after in the sport of professional bodybuilding. However, steroid use often differs significantly between male and female competitors due to biological differences and varying goals. This in-depth guide examines steroid use in bodybuilding across gender, including prevalence, motivations, protocols, health risks, and more.
Table of Contents
TogglePrevalence of Steroid Use among Professional Bodybuilders Females and Men’s is assumed to be high
It is considered an open secret within the sport that the vast majority of IFBB professional bodybuilders, both male and female, use steroids combined with their intense training and rigid nutrition programs to develop extreme physiques far surpassing natural genetic limits.
Some key factors supporting widespread steroid use in professional bodybuilding include:
Enhanced recovery and ability to tolerate extremely heavy training loads and volume
Maximized muscle growth response exceeding what is achievable naturally
Shredded, paper-thin levels of body fat unattainable without chemical assistance
Competitive pressure to match one’s opponents also using steroids
Decreased risk aversion due to immense financial incentives in the sport
Top pros have the resources, expertise, and incentive to implement steroid protocols in conjunction with cutting-edge training and nutrition practices to optimize results. Use begins early in aspiring athletes’ careers.
However, female bodybuilders face greater scrutiny and stigma regarding steroid use compared to their male counterparts, with few openly discussing their protocols. But size and conditioning exhibited on stage makes some degree of chemical assistance apparent at the highest levels.
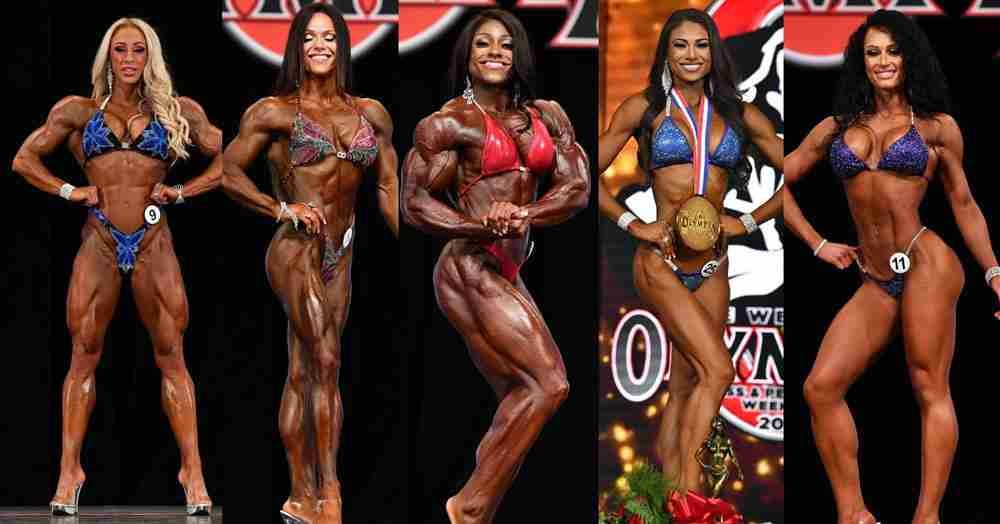

Male and Female Bodybuilders Often Have Vastly Different Goals and Responses to Steroids
While male bodybuilders utilize steroids chiefly to gain large amounts of pure muscle mass well past natural potential while staying lean, common goals among female users are different:
Gaining significant muscle, but not to the degree of most male users
Retaining a feminine, aesthetic physique – avoiding becoming overly muscular or blocky
Burning body fat to achieve extremely ripped conditioning
Minimizing masculine side effects of steroids through prudent compound selection and dosing
The “look” sought after by top female contenders remains markedly more subtle compared to the dramatic mass monsters among male professionals. Lower doses are often favored by women since they are generally more sensitive to anabolic steroids and susceptible to virilization effects. The overall risk-reward balance differs as well between genders.
Biological Differences That Can Make Steroid Use More Problematic For Females
While anabolic steroids offer substantial performance enhancement effects, their use tends to be substantially riskier for women compared to men due to innate biological differences including:
Increased likelihood of experiencing masculinizing effects like voice deepening, facial hair growth, and body hair increases – changes that are permanent and can be extremely distressing
Disruption of menstrual cycles and general fertility due to suppression of natural estrogen and progesterone because of profound hormone imbalances
Potential enlargement of the clitoris and uncomfortable changes in libido
Exacerbated negative impact on cardiovascular markers like cholesterol levels compared to males
Increased risk of lasting complications like acne, scalp hair loss, and changes in breast shape and tissue appearance
These hazards mean managing potential virilization effects requires extreme diligence around component selection, dosing, cycle length, and ancillary drugs. Shorter cycles tend to be favored by female users.

Typical Steroid Options Tend to Vary Between Male and Female Users
While there is crossover, some steroids more commonly used by male and female competitors include:
For Men:
Testosterone – Included in almost all male cycles for its broad efficacy and versatility
Trenbolone – Extremely popular and potent for boosting strength and muscle hardness
Anadrol – Known for producing massive size and weight gains but with harsh side effects
Dianabol – Leads to fast strength and size increases but with more estrogenic activity
For Women:
Primobolan – Valued for adding lean tissue without many masculinizing effects
Anavar – A milder oral anabolic well-suited for beginners and cutting fat
Winstrol – Aids muscle hardening, vascularity, and toning without excessive size
Nandrolone – Provides strength and mass gains with lower estrogenic side effects
Females must select compounds carefully that produce substantial muscle growth without heavy androgenic or estrogenic activity. Testosterone use is rare due to its strong effects on virilization.
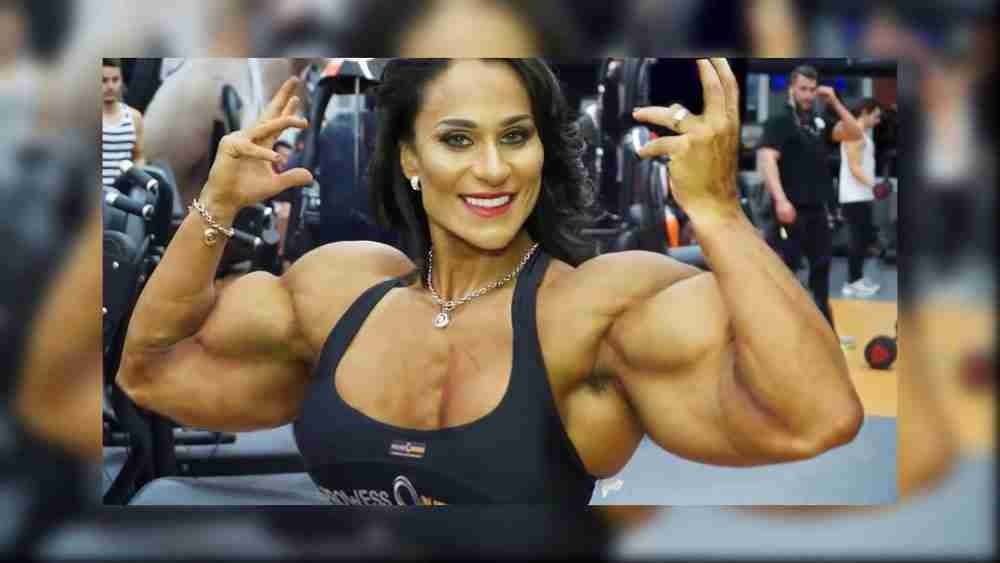

Dosing and Cycling Protocols Also Differ Between Genders
Male bodybuilders often utilize doses at the higher end of effective ranges such as 500-1000+ mg per week for injectables or 30-50+ mg daily for orals. Longer cycles of 12-20+ weeks are also common among males.
In contrast, female users tend to favor much lower, more conservative doses even when aiming to gain significant size. The emphasis is preserving femininity as much as possible. Oral doses rarely exceed 10-20mg and injectables stay in the range of 50-150mg per week. Cycle length is 6-10 weeks for most women.
Men have more flexibility to experiment aggressively and push boundaries with higher doses, stacks, and longer cycle duration thanks to fewer concerns about permanent virilization effects. But health risks remain substantial even with prudent use.
Here are some common dosage ranges for the most popular steroids used by male and female bodybuilders:
For men:
Testosterone (Cypionate, Enanthate, Propionate) – 400-1000mg per week
Trenbolone (Acetate, Enanthate) – 300-700mg per week
Dianabol – 25-50mg per day
Anadrol – 25-100mg per day
Deca-Durabolin – 200-600mg per week
Winstrol – 25-100mg per day
For women:
Anavar – 5-20mg per day
Primobolan – 50-150mg per week
Winstrol – 5-15mg per day
Nandrolone – 50-150mg per week
Testosterone Propionate – 25-50mg per week
Anadrol – 10-25mg per day
Key differences:
Men use much higher doses, on average 2-4x higher than women.
Women rarely use the most potent steroids like Trenbolone due to virilization risks.
Oral doses tend to be lower for women since 17aa steroids are harsher on the liver.
Testosterone is used sparingly by women and mainly in low dose propionate form.
Dosing must be individualized based on goals, genetics, experience level, and sensitives. Starting low and slowly increasing over time helps assess tolerance. There are always risks, but judicious use minimizes side effects. An experienced coach is invaluable for guiding safe cycles.
What is the typical duration of steroid cycles for females and males?
There are some general differences between typical cycle lengths for male versus female steroid users:
For men:
Cycle lengths range from 8-20+ weeks, with 12-16 weeks being most common.
Short cycles around 8 weeks are utilized by beginners or with the harshest compounds.
Moderate cycles tend to span 12-14 weeks for experienced users.
Advanced users often extend cycles to 16-20+ weeks to maximize gains.
Cycle length depends on goals, experience, compounds used, and tolerance.
For women:
Cycles are much shorter for women, averaging 6-10 weeks.
Beginners start with 6 weeks and may gradually extend cycles to 8-10 weeks once comfortable.
Extending past 10 weeks is rare due to increased virilization risks.
Shorter cycles are sometimes implemented for peak conditioning before a competition.
Some women use a lower dose approach indefinitely rather than cycling.
In general, men utilize longer cycle lengths because they can handle higher doses and more potent compounds. Women use conservative doses and limit cycle duration to avoid masculine side effects.
No definitive standards apply – cycle length should be individualized based on your unique response. Starting with shorter cycles as a beginner is advised. An expert can help determine ideal cycle timing.
Both Genders Require Diligent Health Monitoring and Post Cycle Protocols
Despite differences in goals and ideal protocols, both male and female users require extensive health screening and monitoring during use to minimize risks including:
Bloodwork – Tests estrogen & testosterone levels, cholesterol, liver enzymes, etc.
Cardiovascular Monitoring – Blood pressure, heart rate, electrocardiograms, etc.
Side Effect Management – Medications for gynecomastia, acne, virilization, etc.
Cycle Support Supplements – Liver, heart, estrogen protection
Post Cycle Therapy – SERMS, aromatase inhibitors, etc. to normalize hormones
Working closely with a physician knowledgeable in optimizing steroid use can help determine appropriate compound selection, dosing, and cycling practices tailored to the individual based on factors like age, genetics, lifestyle, health status, and sensitives. There is no one-size-fits-all universal approach.
Above all, a healthy lifestyle should be prioritized over success in any physique sport. There are always risks when using powerful drugs like steroids, but working closely with medical experts helps minimize potential harms.
What are the methods of post-cycle therapy for males and females?
There are some key differences between post cycle therapy (PCT) protocols for male and female steroid users:
For men:
Nolvadex is commonly used – typical dosing is 40mg per day tapering down over 4-6 weeks.
Clomid may be used instead of or with Nolvadex at 50-100mg per day for 4-6 weeks.
HCG may be incorporated before SERMs at 500-1000IU 2-3x per week for 2-3 weeks.
Aromatase inhibitors like Arimidex may also be used to control estrogen.
Harsher cycles require more aggressive PCT – longer durations or higher doses.
For women:
Lower doses of SERMs are utilized – Nolvadex at 10-20mg daily or Clomid 25-50mg daily.
SERM use is often shorter as well – 3-4 weeks rather than 4-6 weeks.
HCG is rarely used due to potential hormone fluctuations.
Aromatase inhibitors control estrogen rebound.
Additional medications may be used to restart menstruation.
The goal of PCT is restoring natural hormone production. This process takes longer for women so they tend to use lower SERM doses over shorter periods to avoid side effects. Aggressive PCT can exacerbate hormonal dysfunction if not done properly.
An expert doctor is invaluable for guiding PCT to match the steroid cycle and the individual’s needs. Bloodwork helps fine-tune dosing as necessary. Recovery cannot be rushed – patience is imperative after suppressive cycles.
How much time a female and a male have to wait to start another cycle?
For males:
Most men wait 10-16 weeks between cycles, with 12 weeks being a common length.
This allows enough time for the body to recover normal hormone production and restore physiological functioning after being suppressed during the cycle.
Bloodwork is recommended to confirm the body has recuperated before starting another cycle.
Some men wait shorter or longer durations depending on harshness of compounds, cycle length, and personal recovery rates.
For females:
Women generally need to wait longer between cycles compared to men, often 16 weeks minimum due to greater hormonal sensitivity.
Recovery can take longer because women use lower doses, so suppression may be less pronounced.
Time is required to ensure menstrual cycle regularity before subsequent steroid use.
Bloodwork verification of full recovery is extremely important for women before cycling again.
Some women wait 6 months or longer between cycles to exercise extreme caution.
No set rule applies to all users. Working with a doctor and getting bloodwork guides ideal timeframes. The body must fully normalize before taxing it again with another cycle. Patience is key – rushing cycles increases risks substantially. Err on the side of longer off times, especially for women due to higher margin of error.
Share this page:
- Share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Share on Tumblr (Opens in new window) Tumblr
Written by Steroids USA
Pay with WISE APP or Remitly
Pay with WISE App or Remitly
Fast money transfers from USA for fast delivery of steroids
Secure delivery in USA
100% reliable shipping in USA
24x7 Support
Online 24 hours
Low cost delivery
Great shipping prices in USA
BULK ORDER DISCOUNT
If you are a reseller in the USA you can get a special DISCOUNT, we can give you up to 50% or more on bulk orders. If you want to make a bulk order, we can negociate for orders of over USD$4,000, contact us by email.
Steroids info