Category
- Best Peptides for muscle growth
- Geno Pharma Domestic Warehouse 2 (Canada&USA)
- GPH(Domestic Shipping US) Warehouse 1
- Human Pharma Premium
- Phar Labs Premium-Select
- Steroids on Sale USA, Real Steroids Online
- New arrivals in USA
- Most popular steroids in USA
- Antiestrogens / Gonadotropins
- Bangkok Steroid USA
- Biopharma Steroid USA
- British Dragon
- Anabolic Steroids for Horses
- Fat-burners
- Gen Pharma USA
- Medical Pharma Steroid USA
- Medical Tech Steroid USA
- Novocrine Steroids
- HGH USA
- Omega Labs Steroid USA
- Rotterdam Steroids USA
- SARMs USA
- Sciroxx
- Sydgroup Steroid USA
- Big vetenary Steroid USA
- Watson Steroids
- XT Labs Steroids
Most Popular steroids USA
-
 Primobolan for sale 100mg 10 ml Human Pharma in USA
$115.00
Primobolan for sale 100mg 10 ml Human Pharma in USA
$115.00 -
 NPP Steroid 100mg 10 ml Premium Domestic USA
NPP Steroid 100mg 10 ml Premium Domestic USA
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$80.00Current price is: $80.00. -
 Anavar for Sale in USA – 10mg 80 Tabs GPH-Premium
Anavar for Sale in USA – 10mg 80 Tabs GPH-Premium
$110.00Original price was: $110.00.$80.00Current price is: $80.00. -
 Buy Anavar 10mg – Purchase Geno Pharma
$99.00
Buy Anavar 10mg – Purchase Geno Pharma
$99.00 -
 Testosterone Cypionate Buy 300mg 10ml Geno Pharma
$99.00
Testosterone Cypionate Buy 300mg 10ml Geno Pharma
$99.00 -
 Buy Testosterone E 300mg 10 ml Geno Pharma Domestic USA/CA
$99.00
Buy Testosterone E 300mg 10 ml Geno Pharma Domestic USA/CA
$99.00 -
 Testosterone Cypionate 200 Biopharma 10 amp
Testosterone Cypionate 200 Biopharma 10 amp
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$72.00Current price is: $72.00. -
 Testosterone 400 Biopharma 10 Ampoules
Testosterone 400 Biopharma 10 Ampoules
$99.00Original price was: $99.00.$75.00Current price is: $75.00. -
 Eq 300 steroid Rotterdam 10ml
Eq 300 steroid Rotterdam 10ml
$79.00Original price was: $79.00.$69.00Current price is: $69.00. -
 Steroid Deca Geno Pharma 300mg 10ml
Steroid Deca Geno Pharma 300mg 10ml
$110.00Original price was: $110.00.$99.00Current price is: $99.00. -
 Boldenone Cypionate 200 mg / 10 mL Geno Pharma
Boldenone Cypionate 200 mg / 10 mL Geno Pharma
$90.00Original price was: $90.00.$85.00Current price is: $85.00. -
 Somatrox XT Labs 150 IU x 10 vials (15 ui each)
Somatrox XT Labs 150 IU x 10 vials (15 ui each)
$450.00Original price was: $450.00.$350.00Current price is: $350.00.

IGF-1 LR3 1mg 2 ml Xt Labs: Supercharged Muscle Growth
$150.00 Original price was: $150.00.$130.00Current price is: $130.00.
Share this page:
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window) Tumblr
Long arginine 3-IGF-1, also known as IGF-1 LR3 or LR3-IGF-1, is a synthetic variant and lengthened analogue of human insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) (1),(2), designed to support muscle growth and recovery. It is popular among athletes and bodybuilders for its anabolic properties. Xt Labs is recognized for supplying IGF-1 LR3 with a focus on quality and reliability. This article explores its benefits, usage guidelines, potential risks, and Xt Labs’ role in the market.
Understanding IGF-1 LR3
IGF-1 LR3 is an important compound in the field of health and fitness, particularly known for its role in muscle growth and recovery. This section delves into the essential aspects of IGF-1 LR3, including its definition, differences from IGF-1, and its mechanisms of action.
What is IGF-1 LR3?
IGF-1 LR3, or Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Long Arg3, is a synthetic analog of IGF-1, which is a hormone that plays a critical role in childhood growth and continues to have anabolic effects in adults. This variant has been modified specifically to enhance its bioavailability and potency, allowing for a longer half-life in the body. Unlike its natural counterpart, it binds more effectively to the IGF receptor, which results in increased cellular growth, particularly in muscle tissues.
How IGF-1 LR3 Differs from IGF-1
- Increased Half-Life: LR3-IGF-1 has a much longer half-life than IGF-1, which allows for sustained activity in the bloodstream.
- Enhanced Potency: The molecular modifications of LR3-IGF-1 reduce its binding affinity to insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs), which increases its availability in the bloodstream. This prolonged availability enhances its anabolic effects, as it remains active for a longer period and interacts more consistently with IGF-1 receptors.
IGF-1 LR3 is distinguished from native IGF-1 by two key modifications: the substitution of arginine for glutamic acid at the third amino acid position (“arginine 3”) and the addition of 13 amino acids (MFPAMPLLSLFVN) at its N-terminus. This results in a total of 83 amino acids, compared to IGF-1’s 70. These changes allow LR3-IGF-1 to maintain its receptor agonist properties, minimize binding to IGFBPs, and offer enhanced metabolic stability (1)(2). As a result, LR3-IGF-1 is about three times more potent than native IGF-1 (3) and has an extended half-life of approximately 20 to 30 hours, compared to the 12 to 15 hours of standard IGF-1 (4)
Mechanism of Action
The action of IGF-1 LR3 is primarily through its interaction with specific receptors on cell surfaces, triggering a cascade of biological processes that lead to muscle growth and recovery. This process involves several key mechanisms:
- Protein Synthesis Enhancer: significantly enhances the synthesis of proteins by increasing amino acid uptake in muscle cells, which serves as the building block for muscle growth.
- Muscle Cell Proliferation: It stimulates the differentiation and proliferation of myoblasts, the precursors to muscle cells, further contributing to muscle hypertrophy.
- Reduction of Muscle Breakdown: it may also inhibit pathways that lead to muscle breakdown, promoting an anabolic environment conducive to growth.
By facilitating these mechanisms, LR3-IGF-1 plays a pivotal role in optimizing recovery and enhancing overall performance in physical activities.
Benefits of IGF-1 LR3
IGF-1 LR3 is known for its wide range of benefits that can enhance physical performance and health. This section explores the primary advantages that can be gained through its use.
Muscle Growth and Development
One of the most compelling benefits and its ability to significantly promote muscle growth and development. It enhances protein synthesis, allowing the body to utilize amino acids more effectively to build muscle. Users frequently report:
- Increased Muscle Mass: Users often experience notable gains in muscle mass in a relatively short period.
- Improved Muscle Definition: The compound aids in muscle conditioning, contributing to a more defined physique.
- Enhanced Muscle Strength: As muscle mass increases, so does overall strength, allowing for better performance in physical activities.
Enhanced Recovery
Recovery is a crucial aspect of any training regimen, and plays as pivotal role in enhancing recovery times. It operates by:
- Accelerating Tissue Repair: facilitates quicker repair of muscle fibers after intense workouts, diminishing soreness.
- Reducing Downtime: Athletes can resume training more rapidly due to the improved healing process.
- Supporting Joint Health: By promoting the growth of cartilage and connective tissues, it helps in reducing joint pain and discomfort.
Fat Loss and Lean Body Mass
Another significant advantage of IGF-1 LR3 is its ability to assist with fat loss while preserving lean body mass. This effect can often be attributed to:
- Boosting Metabolism: Increased metabolic rate aids the body in burning fat more efficiently.
- Promoting Fat Oxidation: Users may see improved fat utilization as a source of energy, resulting in fat loss.
- Maintaining Muscle During Caloric Deficits: Users often find they can maintain muscle mass even when cutting calories, leading to an ideal body composition.
Exploring the Anti-Aging Potential of IGF-1 LR3
While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that LR3-IGF-1 may also confer anti-aging benefits. Potential effects include:
- Improved Skin Elasticity: Enhanced collagen production may contribute to a more youthful appearance.
- Enhanced Bone Density: Some research indicates improvements in bone health, which can mitigate age-related bone loss.
- Boosted Overall Vitality: Users often report feeling more energetic, contributing to an enhanced quality of life.
- Cognitive improvements : Research suggests that intranasal LR3-IGF-1 is under investigation and shows partial results indicating potential cognitive improvements. Preliminary findings suggest it might aid in managing amyloid plaques and could be relevant in addressing Alzheimer’s disease. However, these results are not conclusive, and further studies are required to confirm its efficacy and safety for neurodegenerative diseases.
IGF-1 LR3 Usage and Dosage
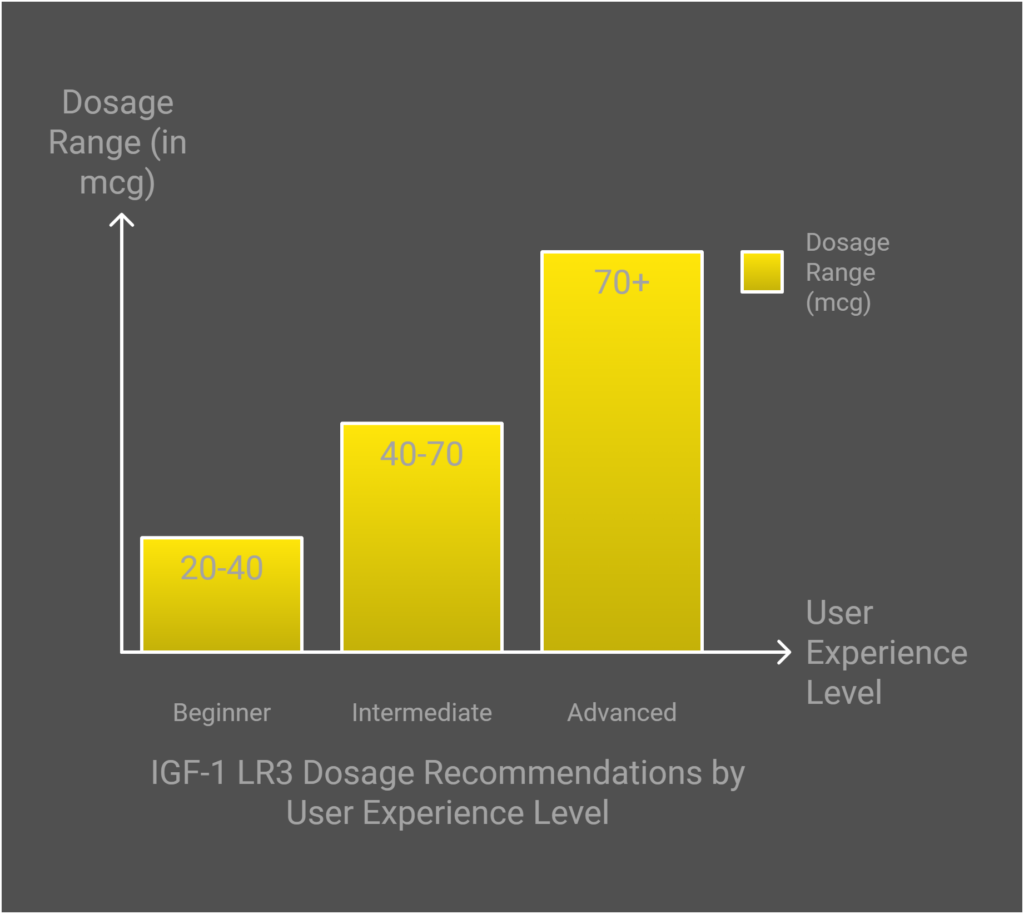
The appropriate usage and dosing of IGF-1 LR3 are critical for maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential risks. The following sections elaborate on dosage guidelines, administration methods, and recommended cycle durations to enhance user experience and effectiveness.
Recommended Dosage Guidelines
Dosing can vary depending on individual goals, body weight, and previous experience with similar substances. Understanding the proper dosage is fundamental to achieving desired outcomes. Generally, the following dosage recommendations are considered effective:
Beginner Dosing
For new individuals new, a dosage of 20 to 40 micrograms (mcg) per day is often advisable. Starting at the lower end allows the body to adapt while monitoring for any side effects.
Intermediate Dosing
Users with some experience may increase their dosage to between 40 to 70 mcg daily. This range typically provides enhanced results in muscle gain and recovery speed.
Advanced Dosing
More seasoned users may opt for dosages from 70 to 100 mcg per day. Regular monitoring is crucial at these higher doses to manage potential adverse effects effectively.
Administration Methods
IGF-1 LR3 is primarily administered through subcutaneous injections, which facilitate optimal absorption into the bloodstream. The administration technique can affect efficacy, hence, understanding proper methods is essential:
Subcutaneous Injection
This is the most common method. It involves injecting the substance into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin. Common sites include the abdomen and thigh area. It’s recommended to rotate injection sites to minimize irritation.
Reconstitution of Peptide
Before injecting, often requires reconstitution with sterile water or bacteriostatic water. Care must be taken to gently swirl rather than shake, preserving the integrity of the peptide.
Cycle Duration
The typical cycle duration ranges between 8 to 12 weeks. Understanding the appropriate cycle length helps in maximizing benefits while reducing potential side effects:
Short Cycles
Some users may choose shorter cycles of 4 to 6 weeks to assess tolerance and response before committing to longer durations. This approach can help in evaluating individual reactions to the peptide.
Extended Cycles
Users aiming for significant muscle gain or recovery may opt for extended cycles of 10 to 12 weeks. Increased monitoring and professional guidance are crucial during these longer periods to avoid accumulating side effects.
Risks and Side Effects
The use of IGF-1 LR3, while associated with various benefits, does carry certain risks and potential side effects. Understanding these aspects is essential for anyone considering its use as a supplement or therapeutic agent.
Potential Side Effects
Users of IGF-1 LR3 may experience a range of side effects stemming from its potent biological activity. Commonly reported side effects include:
- Swelling of Extremities: Retention of fluids can lead to noticeable swelling in hands, feet, or other areas.
- Hypoglycemia: The influence of IGF-1 on insulin can lead to lowered blood sugar levels, necessitating careful monitoring.
- Headaches: Users often report headaches, which may be linked to fluctuations in insulin levels.
- Joint Pain: Some individuals may experience discomfort or pain in their joints after administration.
- Increased Risk of Cancer: There is ongoing debate regarding the association between elevated IGF-1 levels and certain cancers, such as prostate and colorectal cancer. LR3-IGF-1 is often used in research to examine the elevated expression of IGF receptors commonly found in tumor cells. Its role is connected to cyclin D1, a key regulator of the cell cycle that operates via the IGF receptor. This interaction is believed to support tumor growth, improve cell survival, and promote invasive migration. (5)
Long-Term Health Implications
The long-term effects of IGF-1 LR3 use remain a topic of research and concern within the medical community. Possible implications include:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Prolonged use may disrupt normal hormonal signaling, resulting in unwanted health issues.
- Organ Growth: Excessive stimulation of growth factors may lead to abnormal growth in organs, potentially resulting in dysfunction.
- Impact on Metabolism: Changes in metabolic pathways due to high levels of IGF-1 can affect overall health and performance.
- Risk of Dependency: Relying on IGF-1 for muscle growth or recovery can create a psychological dependency on the compound.
Managing Side Effects
To minimize the risks associated with LR3-IGF-1 usage, it is crucial to adopt proper management strategies:
- Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Regular discussions with healthcare providers can help monitor health and manage any emerging side effects effectively.
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: This measure is essential for users susceptible to hypoglycemia, enabling proactive management.
- Adhering to Dosage Guidelines: Following recommended dosages can help mitigate risks; users should avoid exceeding the established limits.
- Timed Cycling: Implementing cycles of usage and taking breaks can reduce the risk of long-term negative effects.
- Awareness and Education: Staying informed about the risks and recognizing side effects early can lead to better health outcomes.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The use of IGF-1 LR3 raises significant legal and ethical questions, particularly within the realm of sports and health regulations. Understanding these implications is essential for users and stakeholders in the fitness community.
Regulation and Legal Status
IGF-1 LR3 is classified differently around the world, and its legality often depends on regional regulations. In the United States, IGF-1 and its derivatives are not approved for over-the-counter sale and are considered controlled substances under certain conditions.
Sports organizations, including the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA), have placed on their list of banned substances. This prohibition is rooted in the potential for unfair advantages in competitive settings, as well as health concerns associated with its non-medical use.
- In some countries, can be obtained legally for research purposes only.
- Users often navigate complex legal landscapes to acquire this compound, which can lead to ethical dilemmas, particularly in professional sports.
- It is advisable for individuals to remain informed about local laws and regulations to mitigate legal risks associated with possession or use.
Ethical Considerations in Sports
The ethical implications of using LR3-IGF-1 in sports extend beyond individual athletes to affecting the integrity of competitive environments. The adoption of performance-enhancing substances raises critical issues about fairness and the spirit of sportsmanship.
Key ethical concerns include:
- Pressure to Perform: Athletes may feel compelled to use substances like IGF-1 LR3 to keep up with competitors, leading to a culture of doping.
- Health Risks: The potential for serious health consequences from long-term use of anabolic substances creates ethical dilemmas for coaches and trainers who may encourage or turn a blind eye to such practices.
- Impact on Youth Sports: The normalization of performance enhancers can influence younger athletes, who might prioritize winning over health and fair play.
As a result, many sporting organizations strive to instill values of ethics and integrity, encouraging athletes to achieve success through natural means. Continuous conversation about these topics is necessary to foster healthy competition and protect the well-being of athletes across all levels.
Table 1: IGF-1 LR3 vs. HGH Comparison
| Aspect | IGF-1 LR3 | HGH (Human Growth Hormone) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Directly binds to IGF-1 receptors, bypassing natural IGF-1 binding proteins for enhanced anabolic effects. | Stimulates the liver to produce natural IGF-1, indirectly supporting muscle growth. |
| Half-Life | Longer half-life (20-30 hours), requiring less frequent administration. | Shorter half-life, typically requiring daily injections. |
| Primary Use | Muscle growth, recovery, and enhanced cellular proliferation. | Broad applications, including growth deficiencies, anti-aging, and general recovery. |
| Risks | Increased risk of cancer and hypoglycemia; promotes cellular proliferation aggressively. | Potential insulin resistance, joint pain, and organ growth with prolonged use. |
| Accessibility | Mostly available for research purposes; legality varies by country. | Approved for medical use in many regions but regulated. |
Table 2: IGF-1 LR3 vs. SARMs Comparison
| Aspect | IGF-1 LR3 | SARMs (Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Promotes cellular growth through IGF-1 receptor activation, enhancing anabolic activity directly. | Selectively targets androgen receptors to promote muscle and bone growth with reduced side effects. |
| Primary Use | Muscle growth, fat loss, and recovery enhancement. | Muscle hypertrophy, fat loss, and preservation of lean mass with minimal hormonal impact. |
| Half-Life | Longer half-life allows for less frequent administration. | Varies depending on the compound, typically shorter than IGF-1 LR3. |
| Risks | Potential for uncontrolled cellular growth, hypoglycemia, and cancer risk. | Hormonal imbalance, liver toxicity (in some SARMs), and cardiovascular effects. |
| Legality and Research | Used primarily in research settings; legal status varies globally. | Many SARMs remain unapproved for human use, with legal restrictions in several regions. |
| Effectiveness | High anabolic potency; significant impact on recovery and muscle growth. | Targeted anabolic effects; often considered safer for non-medical use. |
Comparing IGF-1 LR3 with Other Compounds
The comparison with other compounds highlights its unique properties and mechanisms of action. Understanding how it stacks up against alternatives such as Human Growth Hormone (HGH) and Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) can provide insight into its effectiveness and risks.
Comparison IGF-1 LR3 vs. Human Growth Hormone
IGF-1 LR3 and Human Growth Hormone (HGH) are both influential in muscle growth and recovery, yet they function in distinct ways.
Mechanism of Action
HGH stimulates the liver to produce insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which in turn facilitates muscle growth and repair. On the other hand, LR3-IGF-1 provides similar growth-promoting effects directly, making it potentially more effective for certain users.
Duration and Stability
Has a significantly longer half-life compared to HGH, which allows for less frequent administration. This characteristic may attract athletes looking for convenience in their regimen.
Side Effects
While both compounds can lead to side effects like joint pain and insulin resistance, it is associated with a unique risk profile, including potential water retention and varying impacts on blood sugar levels.
IGF-1 LR3 vs. SARMs
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) are a newer class of compounds that have gained popularity due to their targeted action, but they differ from LR3-IGF-1 in significant ways.
Pursuit of Goals
SARMs are often favored for their anabolic effects without the androgenic side effects seen in traditional anabolic steroids. While they primarily focus on muscle hypertrophy, LR3-IGF-1 also improves recovery times and offers various metabolic benefits.
Research and Approval Status
Many SARMs remain unapproved for human use and lack extensive research studies, unlike LR3-IGF-1, which has seen broader applications in both research and some clinical settings. This difference may reflect on user preferences concerning safety and efficacy.
Effects on Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar
Comparing with other compounds also involves examining their effects on cardiovascular health and metabolism.
Blood Pressure
IGF-1 LR3 may influence blood pressure indirectly through its effects on body composition and muscle mass. An increase in lean muscle can help manage blood pressure, whereas compounds like SARMs generally have variable reports on their impact on cardiovascular function depending on individual responses.
Blood Sugar Levels
IGF-1 LR3 has been noted to lower blood sugar levels, which can be beneficial for some users but may pose risks for individuals with preexisting conditions. Conversely, SARMs tend to have less documented influence on blood sugar regulation, which could be advantageous for those concerned about insulin sensitivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding IGF-1 LR3, covering essential concerns about its effects, potential risks, and guidelines for usage. The following subsections provide detailed answers to frequently asked questions.
Can IGF-1 LR3 Improve Insulin Sensitivity?
Research suggests that IGF-1 LR3 may play a role in enhancing insulin sensitivity, primarily through its effects on muscle tissue. By promoting muscle growth, this compound can increase the uptake of glucose into muscle cells, potentially leading to better insulin responsiveness. This is beneficial for overall metabolic health.
However, the effectiveness of LR3-IGF-1 in improving insulin sensitivity can vary among individuals. Factors such as diet, exercise, and overall health status may influence results. It’s important to approach the use of IGF-1 LR3 with proper understanding and possibly under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Are There Risks of IGF-1 LR3 Leading to Cancer?
The relationship between LR3-IGF-1 and cancer risk remains a topic of ongoing research. Some studies have indicated that elevated levels of IGF-1 may be associated with an increased risk of certain cancers(5), particularly prostate and colorectal cancer. This is thought to be due to IGF-1’s role in promoting cell growth and proliferation.
It’s crucial for users to be aware of these potential risks. Individuals with a history of cancer or those at higher risk should exercise caution and consult with a healthcare provider before using IGF-1 LR3. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of health status are recommended for anyone considering its use.
How Does IGF-1 LR3 Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
IGF-1 LR3 can influence blood sugar levels through its insulin-like actions. By enhancing muscle glucose uptake and promoting glycogen storage, it may help in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. However, improper dosing can lead to hypoglycemia, especially if combined with other medications that lower blood sugar.
Users should be vigilant about their blood sugar levels, especially if they have pre-existing conditions such as diabetes. Monitoring can help mitigate the risk of severe drops in glucose that may result from use.
Who Should Avoid IGF-1 LR3?
Certain individuals are advised to avoid it due to potential health risks. Those who fall into the following categories should exercise caution:
- Individuals with a personal or family history of cancer.
- People suffering from diabetes or other metabolic disorders.
- Those who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Individuals with heart, liver, or kidney issues.
- Anyone taking medications that affect blood sugar levels.
Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is essential for anyone considering, especially for those in the above categories. Personalized assessments can help determine the most appropriate course of action. For more information click here : Peptides for muscle growth
References :
(1) Tomas FM, Lemmey AB, Read LC, Ballard FJ (1996). “Superior potency of infused IGF-I analogues which bind poorly to IGF-binding proteins is maintained when administered by injection”. J. Endocrinol. 150 (1): 77–84. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1500077. PMID 8708565.
(2) Mohan S, Baylink DJ (2002). “IGF-binding proteins are multifunctional and act via IGF-dependent and -independent mechanisms”. J. Endocrinol. 175 (1): 19–31. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1750019. PMID 12379487.
(3) Tomas FM, Knowles SE, Owens PC, Chandler CS, Francis GL, Read LC, Ballard FJ (1992). “Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and especially IGF-I variants are anabolic in dexamethasone-treated rats”. Biochem. J. 282 ( Pt 1) (Pt 1): 91–7. doi:10.1042/bj2820091. PMC 1130894. PMID 1371669.
(4) von der Thüsen JH, Borensztajn KS, Moimas S, van Heiningen S, Teeling P, van Berkel TJ, Biessen EA (2011). “IGF-1 has plaque-stabilizing effects in atherosclerosis by altering vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype”. Am. J. Pathol. 178 (2): 924–34. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.10.007. PMC 3069834. PMID 21281823.
(5) Haluska P, Carboni JM, Loegering DA, et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of the dual insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS-554417. Cancer research. 2006;66(1):362-371.
(6) Engel, M. G. (2023). Deciphering the Role of Insulin and IGF-1 in Brain Aging, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Vascular Dementia. Albert Einstein College of Medicine.
Dr. Daniel Martínez MD, is an endocrinologist and nutrition specialist with over 20 years of experience in managing hormonal and metabolic health. In addition to his clinical practice, Dr. Martínez is dedicated to scientific research focusing on the interaction between endocrinology and performance enhancement. He has co-authored a peer-reviewed article on the medical applications in bodybuilding, bridging the gap between science and athletic performance.
Related products
Stanoplex 5mg XT Labs 100 pills
$73.00Original price was: $73.00.$65.00Current price is: $65.00.Add to cartManufacturer: XT Labs
Pharmaceutical name: Stanozolol
Pack: 5mg 100 tabs
Winstrol is a steroid compound that is available as both an oral and injectable. It is most often used as cutting agent because it doesn’t produce huge weight gains and it also reverses some of the bloated look of testosterone and replaces it with a dry look.
Side effects of this drug include liver toxicity, increased cholesterol, cardiac hypertrophy (enlarged heart) and some users have even reported problems with the joints. Also, the injectable form is quite uncomfortable and can cause pain at the injection site.
Mastaplex XT Labs 100mg 10ml -Steroid USA
$77.00Add to cartMasteron is a derivative of DHT (as you can tell from its chemical name: 2a-methyl-dihydro-testosterone propionate), but what they don’t tell you is that DHT and its derivatives are commonly used in the treatment of certain forms of breast cancer (see etymology here: Mastectomy, Gynocomastia, MASTeron, get it?). Masteron is not used clinically for weight gain so this makes it a very unique steroid from that perspective. Unfortunately, much of the information on Masteron available in medical journals does not focus on weight or strength gains or even fat loss, for those reasons.
Trenboplex XT Labs 100mg 10ml
$77.00Add to cartFor intramuscular injection, contains Trenbolone Acetate. Tenbolone Acetate is a fast acting injectable steroid.
To increase its effective half life, Trenbolone is not used in an unrefined form, but is administered as Trenbolone Acetate Enanthate or Hexahydrobenzylcarbonate. Trenbolone is then produced as a metabolite by the reaction of these compounds with the androgen receptor.
TITAN 400 XT 10ml For Sale USA
$79.00Add to cartExperience the power of TITAN 400 XT Labs, a robust steroid mix designed for serious muscle gains and performance enhancement. Combining 200mg of Testosterone Enanthate, 100mg of Drostanolone Enanthate, and 100mg of Trenbolone Enanthate, this blend is perfect for bodybuilders and athletes aiming for peak results in muscle mass and strength. Ideal for pre-competition and cutting cycles.
Pay with WISE APP or Remitly
Pay with WISE App or Remitly
Fast money transfers from USA for fast delivery of steroids
Secure delivery in USA
100% reliable shipping in USA
24x7 Support
Online 24 hours
Low cost delivery
Great shipping prices in USA
BULK ORDER DISCOUNT
If you are a reseller in the USA you can get a special DISCOUNT, we can give you up to 50% or more on bulk orders. If you want to make a bulk order, we can negociate for orders of over USD$4,000, contact us by email.
Steroids info