Category
- Human Pharma Premium
- Phar Labs Premium
- Steroids on Sale USA, Real Steroids Online
- New arrivals in USA
- Most popular steroids in USA
- Antiestrogens / Gonadotropins
- Bangkok Steroid USA
- Biopharma Steroid USA
- British Dragon
- D & H Denkall Steroid USA
- Fat-burners
- Gen Pharma USA
- Medical Pharma Steroid USA
- Medical Tech Steroid USA
- Novocrine Steroids
- HGH USA
- Omega Labs Steroid USA
- Rotterdam Steroids USA
- SARMs USA
- Sciroxx Steroid USA
- Sydgroup Steroid USA
- Big vetenary Steroid USA
- Watson Steroid For Sale
- XT Labs Steroids
Most Popular steroids USA

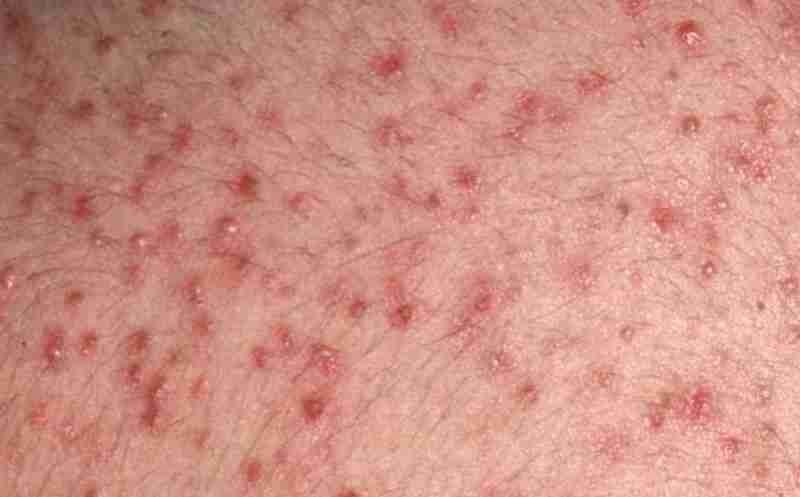
Treatment for acne caused bt steroids
Effects of anabolic steroids on the skin
The abuse of anabolic steroids also increases the secretion of sebaceous glands (which are found mainly on the face, upper trunk, shoulders, and upper back) and their size. “This translates into skin and oil problems, which in severe cases can evolve into acne conglobata like the clinical case [in ‘The Lancet’] and even acne fulminans,” .
“Acne appears in 45% of those who abuse anabolic-androgenic steroids”
Acne fulminans (AF) is a rare and very severe form of acne characterized by the sudden onset of painful, ulcerative pustules and associated systemic symptoms. Recommended treatment is a combination of oral steroids and isotretinoin. We report the case of a male patient with poor response to this treatment who was successfully treated with the combination of oral cyclosporine and isotretinoin.
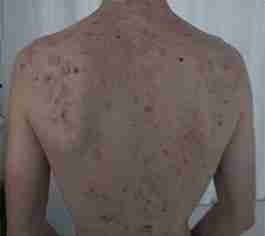
A 15-year-old white male patient with severe acne flare was referred to our hospital. Diagnosis was acne vulgaris for the past 2 years, treated with topical antibiotics. Six months before the consultation, the lesions worsened and a diagnosis of acne conglobata was made. He was treated with isotretinoin 20 mg/day and prednisone 15 mg/day, but there was no clinical improvement. Isotretinoin dosage was increased to 30 mg/day, but 3 weeks later multiple reddish papulonodular and ulcerated lesions with hemorrhagic crusts suddenly developed on his face, neck, and trunk. The lesions were painful, and arthralgias and temperature up to 39°C were noted (Fig 1). Abnormal laboratory findings included elevated C-reactive protein levels (5 mg/dL; normal < 1 mg/dL) and leukocytosis (15,700 cells/mm3) with neutrophilia (68.8%). AF was diagnosed, and treatment with prednisone 60 mg/day and isotretinoin 20 mg/day was initially successful. Nevertheless progressive worsening was observed in the following weeks while prednisone was tapered and isotretinoin increased to 30 mg/day. He was treated with potassium permanganate baths and topical antibiotics. Oral cyclosporine 5 mg/kg/day plus isotretinoin 30 mg/day was initiated and systemic steroids were stopped. After a few weeks, the lesions improved, and 4 months later, cyclosporine was discontinued. A total dose of isotretinoin 100 mg/kg could be completed, and he presented an almost complete resolution of the inflammatory lesions with some residual scarring (Fig 2). No significant side effects or laboratory abnormalities were observed during treatment.
Fig 1 Acne fulminans. Initial presentation with draining pustules and crusted papules and nodules on the back.
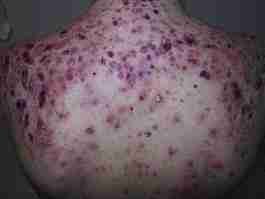
Fig 2 Acne fulminans. Complete resolution of the inflammatory lesions with residual scarring after treatment with cyclosporine and isotretinoin.
AF is a rare condition that is considered the most severe form of acne. It is characterized by a sudden onset of ulcerative, crusty, painful lesions. Most patients are young teenagers with previous mild to moderate acne. It is considered a severe inflammatory disease with abscess formation and hemorrhagic crusts accompanied by high temperature, asthenia, anorexia, and often asymmetric polyarthralgias.
In this case, laboratory findings showed an intense neutrophilic leucocytosis and elevation of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein. The etiology of AF is appears to be multifactorial.
The diagnosis is usually clinical. The differential diagnosis includes other disorders such as PAPA syndrome and SAPHO syndrome.
Oral antibiotics are usually ineffective. The combination of oral isotretinoin and systemic corticosteroids is the treatment of choice, but recurrences are not unusual when steroid dose is tapered. We have found only 1 report describing a good response of AF to a combination of cyclosporine and prednisolone.
To our knowledge this is the first report showing a good response to cyclosporine combined with isotretinoin. Because this regimen has a very good short-term safety profile (particularly in young persons), it can be an alternative in patients with AF when systemic steroids are either ineffective or contraindicated.
In acne vulgaris, excessive secretion of sebum from sebaceous glands is accelerated by conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by type I 5α reductase that is strongly expressed on sebaceous glands.[3] Therefore, inhibitory reagents of type I 5α-reductase have a potential to improve acne vulgaris. Type I 5 α reductase inhibitor (compound A, 25 mg once daily) has been used for the patient with acne vulgaris.[4] In this study, selective type I inhibitor “compound A (25 mg/day)” was ineffective in the treatment of acne vulgaris. However, it might be different from dutasteride because the applied dose was very different between compound A (25 mg/day) and dutasteride (0.5 mg/day). Dutasteride is a potent type I 5α-reductase inhibitor that has recently been approved for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).[5] In the pathogenesis of AGA and BPH, DHT is a key androgen, which is downregulated by dutasteride. Here, we show two AGA patients treated with dutasteride. It is noted that dutasteride also exerted a beneficial therapeutic effect on their concomitant acne vulgaris.
Share this page:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
Written by Steroids USA
Pay with Cash App or Remitly
Pay with Cash App or Remitly
Fast money transfers from USA for fast delivery of steroids
Secure delivery in USA
100% reliable shipping in USA
24x7 Support
Online 24 hours
Low cost delivery
Great shipping prices in USA
BULK ORDER DISCOUNT
If you are a reseller in the USA you can get a special DISCOUNT, we can give you up to 50% or more on bulk orders. If you want to make a bulk order, we can negociate for orders of over USD$4,000, contact us by email.